India Surpasses Japan in Asia Power Index
In a significant geopolitical shift, India has surpassed Japan and has become the third most powerful country in Asia according to the esteemed Asia Power Index. This development marks a pivotal moment in India's ascent on the global stage and reflects the changing dynamics of power in the Asia-Pacific region. This accomplishment is a reflection of India’s growing economic prowess, dynamic diplomacy, and strategic influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
Losers and gainers
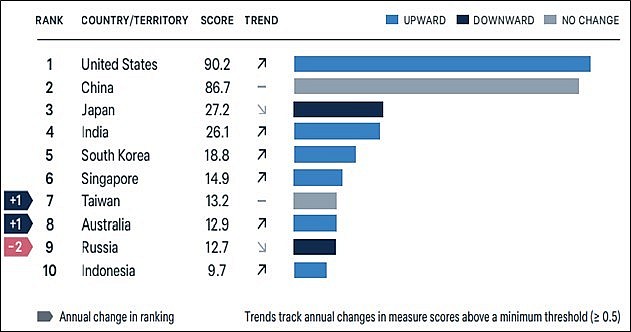 |
Asia Power Index is yearly evaluation, which was started by the Lowy Institute in 2018, has established itself as a standard for gauging power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific area. The index assesses 27 nations using eight thematic metrics. It employs 131 distinct indicators, split into determinants based on influence and determinants based on resources, spread across eight thematic measures:
Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability- Measures core economic strength, connectivity, and technological sophistication, through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP)
- Military Capability- Assesses conventional military power, defense spending, and strategic assets.
- Resilience- Evaluates a nation’s ability to withstand external pressures and maintain stability.
- Future Resources- Forecasts the future distribution of economic, demographic, and military resources.
Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships- Assesses the capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks- Assesses the strength and breadth of military alliances and partnerships.
- Diplomatic Influence- Gauges a country’s engagement in international diplomacy and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence- Measures a nation’s ability to shape international public opinion through culture and media
This multifaceted approach allows for a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific region.
India's Ascent: Key Factors and Achievements
India's rise to the third position in the Asia Power Index is not a sudden development but the result of steady progress across multiple fronts.
1. Economic growth and resilience--the engine of power
India's ascent in the Asia Power Index has been largely attributed to its economic growth. The nation's economic capability demonstrate its robust post-pandemic recuperation. India, one of the main economies with the highest rate of growth in the world, has strengthened its position as the third-largest economy in terms of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), which has increased its power in Asia.
Scores of performance
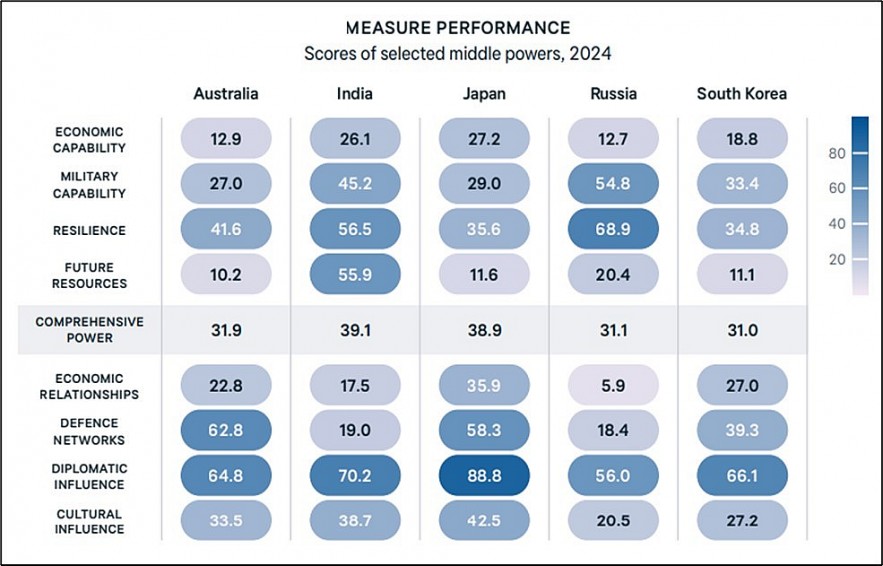 |
India's impressive economic resiliency is especially noteworthy in light of the recent global problems. India has maintained strong GDP growth despite global concerns; during the next ten years, this growth is expected to average between 6 and 7 percent annually. With the help of growing infrastructure, a booming digital economy, and robust domestic consumption, India surpassed the UK to become the world's fifth-largest economy in 2023.
This sustained economic growth has been fueled by the government's focus on reforms such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and initiatives like "Make in India" and "Digital India," which have improved the country’s investment climate. With a youthful and increasingly tech-savvy population, India is poised to lead sectors like information technology, e-commerce, and renewable energy. The Indian economy is on a path to becoming a global economic powerhouse in the coming years.
2. Future potential and demographic dividend
India's future resources is one of the most encouraging aspects of the country's rise. This indicator shows how much India can do in the next few decades to take advantage of its demographic dividend. India has an advantage over many of its regional rivals, especially China and Japan, in that its young population is projected to fuel economic growth and labor force expansion for many years to come.
India is well-positioned for long-term economic and geopolitical dominance thanks to its population advantage. The ageing populations and declining workforces of other major countries in the region provide obstacles, but India's growing pool of young, skilled workers has the potential to become a major worldwide source of talent and innovation. India will continue to profit from its demographic dividend thanks to government policies that support education, skill development, and innovation in addition to this advantage.
3. Military modernization--strengthening strategic posture
India's military prowess is a critical factor in its rise in the Asia Power Index. The nation has progressively upgraded its defense capabilities, rising to the position of fourth in the world for military spending. While not the primary driver of India’s rise, its growing defense capabilities and nascent arms export industry have bolstered its standing.
India's strategic outreach in the Indo-Pacific region has found a significant instrument in the Indian Navy. India has demonstrated its commitment to securing vital maritime lanes by the commissioning of indigenous aircraft carriers like INS Vikrant and the growth of its submarine fleet. Along with major modernization, the Indian Air Force now possesses indigenous systems like the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas and fighter fighters like the Rafale.
Furthermore, India’s defense networks have expanded through deeper strategic partnerships with countries like the United States, Australia, Japan, and France. India's participation in security dialogues like the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) has underscored its commitment to regional security and stability. Collaboration with the Quad emphasizes principles such as freedom of navigation and a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific—central tenets of India’s foreign policy.
India’s defense modernization is further complemented by its growing arms export industry. While still modest, India’s successful defense exports, such as the BrahMos missile deal with the Philippines, signal its potential to become a significant player in the global arms market. These developments enhance India’s economic prospects while strengthening its strategic partnerships in the region.
4. Diplomatic influence and strategic autonomy
India’s foreign policy, under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has seen a marked increase in its global recognition and diplomatic clout. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed it to maintain relationships across diverse geopolitical blocs, ensuring a balanced approach in international diplomacy. This strategic autonomy has been a key factor in India’s growing influence in Asia.
India’s diplomatic prowess is evident in its ranking as the sixth most active country in diplomatic dialogues in 2023. India has proactively engaged in multilateral forums such as the United Nations, G20, BRICS, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO). Its participation in groupings like the Quad, where it works alongside the U.S., Japan, and Australia, highlights its commitment to maintaining regional stability in the Indo-Pacific.
India’s growing diplomatic footprint has further been bolstered by its leadership in climate action and development initiatives. For instance, India's role in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) demonstrates its commitment to global challenges such as climate change and sustainable development. Through these initiatives, India is positioning itself as a responsible global player and a leader in fostering regional and international cooperation.
5. Cultural influence and global diaspora- expanding soft power
India’s ascent in the Asia Power Index is not just driven by hard power; it is also rooted in its rich cultural heritage and soft power. The country’s score in Cultural Influence has remained consistently strong, supported by its vast global diaspora and the global popularity of its cultural exports.
India's global cultural footprint is evident in the widespread influence of Bollywood films, yoga, and Indian cuisine. The success of Indian cinema in international markets and festivals, coupled with the global embrace of yoga, has strengthened India’s soft power. The celebration of International Yoga Day, for example, highlights India's ability to shape global cultural trends. These cultural assets enhance India’s global image and complement its geopolitical influence.
The Indian diaspora, one of the largest in the world, has been instrumental in promoting India's interests abroad. With Indian-origin leaders, technocrats, and entrepreneurs contributing to the global economy, the diaspora has become a vital asset for India’s foreign policy. Their success stories not only reflect India’s growing influence but also act as a bridge between India and their host nations.
6. Technology and innovation: leading the digital future
India’s leadership in technology and innovation has been another key driver of its rise in the Asia Power Index. As one of the world’s leading information technology hubs, India’s IT sector accounts for a significant portion of its GDP. Companies like Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Infosys, and Wipro are global leaders in software services, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing.
India’s digital transformation initiatives, such as Digital India, have revolutionized governance, financial inclusion, and service delivery. The rapid growth of internet penetration and mobile technology has made India one of the largest digital markets in the world. Platforms like UPI (Unified Payments Interface) and Aadhaar have transformed the way Indians access financial services, setting a global benchmark for digital payments and identity management systems.
Moreover, India is making strides in frontier technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and space exploration. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has achieved significant milestones, including the successful launch of Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan missions. ISRO’s cost-effective space missions have attracted global collaboration, establishing India as a major player in space exploration.
India’s leadership in renewable energy, particularly in solar energy production, further highlights its role in driving global sustainability. As one of the largest producers of solar energy, India is setting ambitious targets to combat climate change and transition to clean energy solutions.
Implications for Regional Dynamics
India's ascent to the third position in the Asia Power Index, surpassing Japan, has significant implications for the geopolitical landscape of the Asia-Pacific region:
- Shifting balance of power: This change reflects a broader shift in the balance of power in Asia. As India's influence grows, it could lead to a recalibration of regional alliances and partnerships.
- Counterbalance to China: India's rise provides a potential counterweight to China's dominance in the region. This could lead to more balanced regional dynamics and potentially mitigate concerns about a unipolar Asia.
- Enhanced Role in Regional Security: With its growing economic and diplomatic clout, India is likely to play an increasingly important role in regional security arrangements. Its participation in the Quad and other multilateral forums could become more influential.
- Economic Opportunities: India's economic growth and large consumer market present significant opportunities for regional and global businesses. This could lead to increased economic integration within Asia and beyond.
- Demographic Advantage: India's youthful population contrasts sharply with the aging demographics of many East Asian countries. This could lead to shifts in regional labor markets and economic dynamics over the coming decades.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, India's trajectory in the Asia Power Index appears promising. With continued economic growth, diplomatic engagement, and strategic autonomy, India is well-positioned to expand its influence in the years to come. The country's rising Diplomatic Influence score and its potential to leverage its demographic dividend suggest that India's role in shaping the future of the Indo-Pacific region will only grow stronger.
Conclusion
A significant turning point in India's rise to prominence as a world power has been reached when it surpassed Japan to take the third spot in the Asia Power Index. This achievement is indicative of India's increasing economic might, diplomatic clout, and untapped potential. As the geopolitical landscape of Asia continues to evolve, India's role as a key player in shaping regional dynamics is set to expand.
In addition to showcasing India's accomplishments, the 2024 Asia Power Index ushers in a new phase of Asian geopolitics. The World will be closely watching India as it negotiates its new role and adds to the intricate web of Asian and international politics as power equations continue to change.
