Interesting Facts About Vietnam's Largest Provinces
| 10 Scenic Vietnamese Spots for Post-Covid Travel | |
| Spectacular Giant Honeybee Nests Hanging on Cliffs in Cao Bang | |
| Run Through the Jungle: The Best Outdoor Activities in Vietnam |
 |
| Photo: VnExpress |
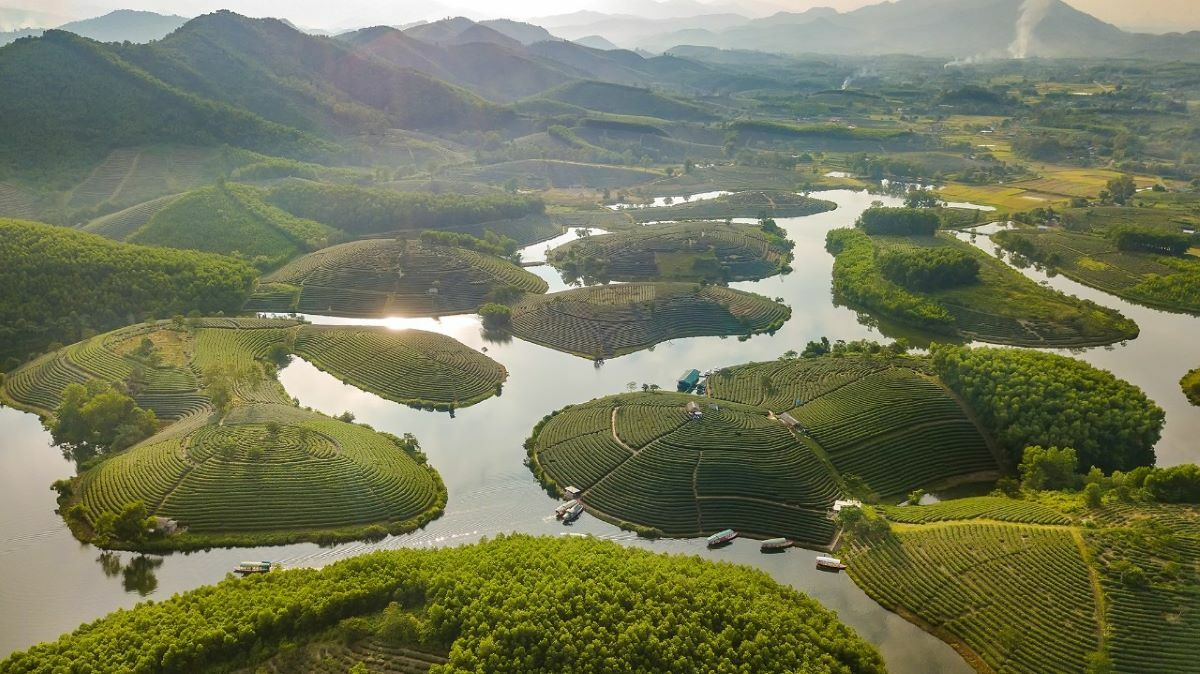
Nghe An Province: With a total area of 16,470 km2 of which 12,000 is forests and mountains, Nghe An is the biggest province in the North Central Vietnam.
It adjoins Thanh Hoa Province to the North, Ha Tinh Province to the South, Laos to the West, and the East Sea to the East. Vinh, the capital city and also the largest city of Nghe An, is located 291km to the South of Hanoi. Interestingly, Nghe An Province and Ha Tinh Province used to be called Nghe Tinh Province from 1976 to 1991. Not until then were the two of them separated and renamed as nowadays.
As Nghe An is parts of the giant Truong Son Mountain Range, 83% of its area is mountainous, making its topography highly complicated. The terrain has a descending slope from North-West to South-East; is separated by mountains, hills, rivers, streams, etc. into many small valleys. In terms of height, the 2,711m high Pulaileng Peak in Ky Son District is most noticeable, while the 0.2m high plains in Yen Thanh Districts are the most humble. Besides, Nghe An also has a highly dense system of rivers with a total length of 9828km. The biggest river is Ca River (also known as Lam River) which actually originates from Laos. The coastline of the province is 82km with 6 watercourse-mouths which allow seaports and sea transportation to develop conveniently.
 |
| Photo: VnExpress |
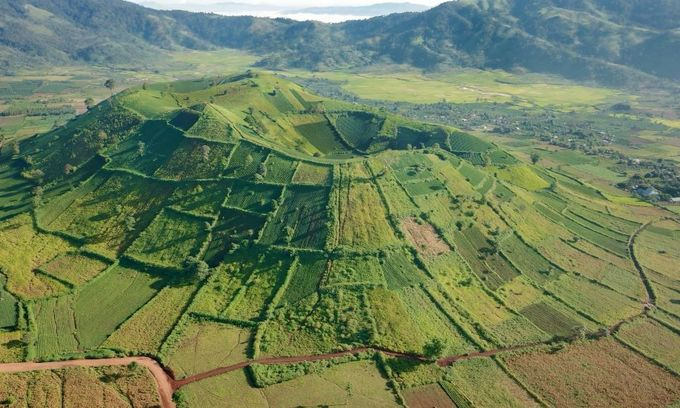
Gia Lai (15.536,9 km2) is a province in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. It is the second-largest province of Vietnam. The name comes from the Jarai people, one of the local indigenous groups.
Gia Lai has many beautiful landscapes. Kon Chu Forest is a protected area for wild animals. Other sites include the Ayunpa military base and villages of Ba Na ethnic group. Coming to Gia Lai, visitors have a change to discover many impressive, poetic scenes. They are Kon Ka Kinh, Kon Cha Rang tropical forests, Xung Khoeng Waterfall, Phu Cuong Waterfall, Da Trang, Mo springs and Ayaun Ha Lake. Located on the top of an extinct volcano, Bien Ho (To Nung Lake) is called the 'Pearl of Pleiku'. Its water is so clear that visitors can see fish swimming under blue water.
 |
| Photo: Wikipedia |
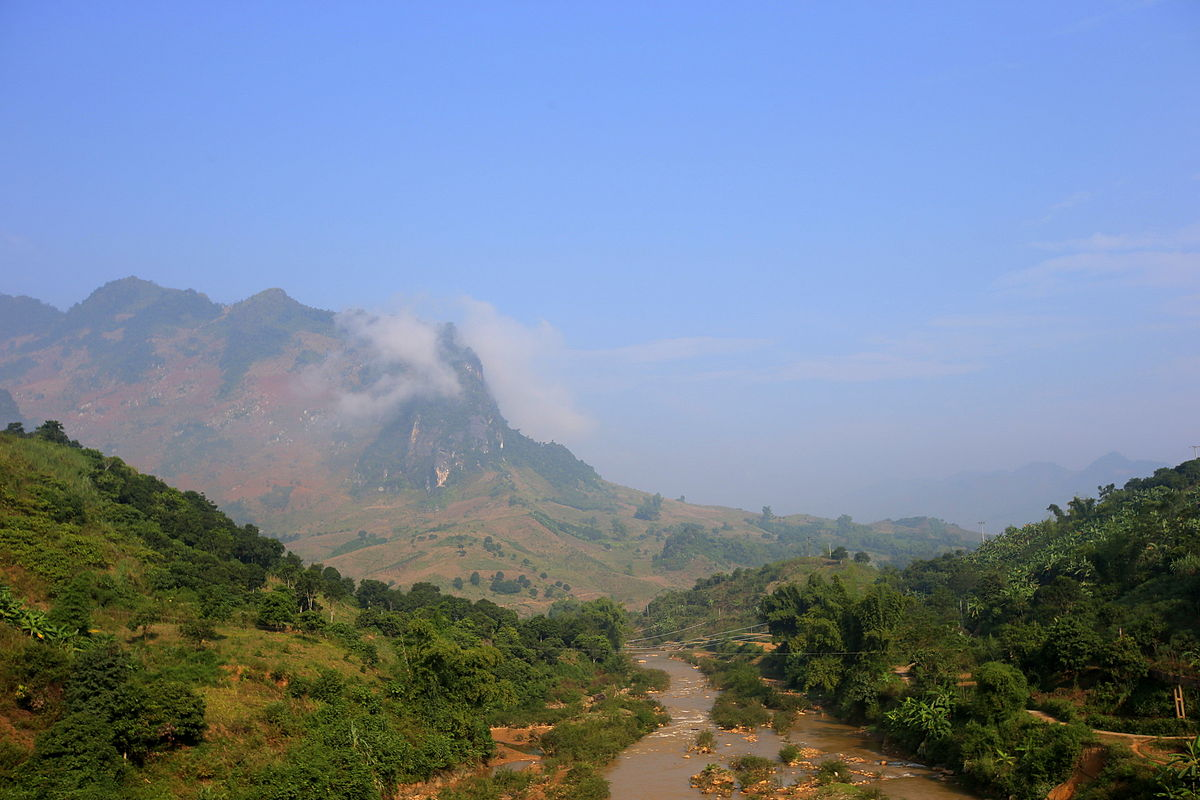
Son La (14.174,4 km2) holds in itself more than just tourism values. It is the home of honorable history, of varied culture, and gentle nature.
With 12 ethnic groups (Thai, Mong, Muong, Tay, etc) that long inhabited the great land, the province can provide a series of Northwest identities. From the colorful dance of embroidered dresses, the warming sound of traditional songs, the ecstatic smell of mountain wine, to various unique customs, all perform fantastically under the cover of majestic landscape.
The climate in Son La is mainly comfortable plus a little chill at the end of the year. Winter is cold and dry. Summer is hot and wet. The temperature may range under 14 degrees at the lowest and reach over 30 degrees at peak.
In summer, around June to August, the rain rate increases dramatically. With a high chance of showers, and if not, is the scorching heat, this time should be avoided in your travel plan.
 |
| Photo: Daktip |
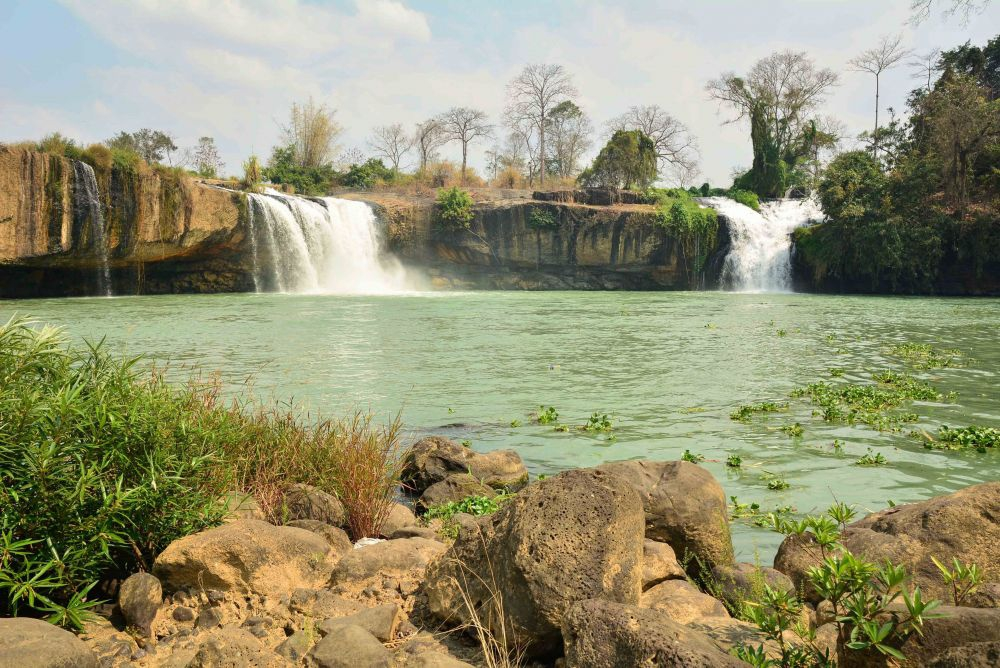
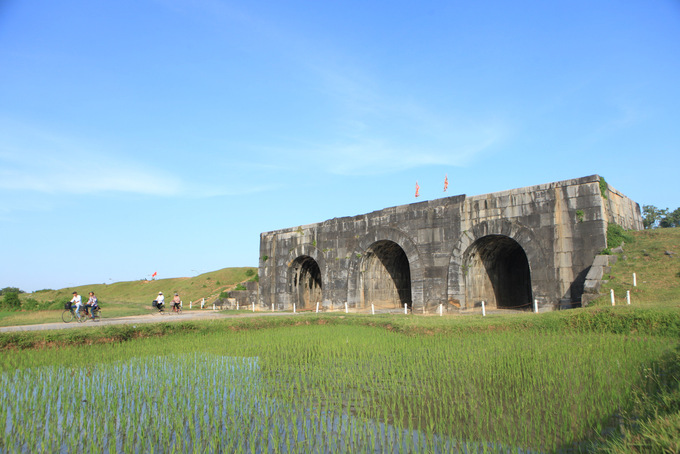
Dak Lak (13.125,4 km2): Located 1410 km from Hanoi and 320 km from Ho Chi Minh, the capital city of Dak Lak - Buon Ma Thuot, might be one of the most famous destinations in Vietnam and the place where you can find the best coffee in South East Asia.
Dak Lak Province spreads out on an area of 13085 km2 (3.9% area of the whole country). A part of the southwest slope of the Annamite Range, Dak Lak has a mostly mountainous topography (35% of its area are highlands and mountains). The average height is from 1000 to 1200 m; the highest peaks are Chu Yang Sin (2442m), Chu H’mu (2051m), Chu De (1793m), and Chu Yang Pel (1600m). In the middle of Dak Lak, one can find a flat stretch of highland which covers 53% of the natural area, with an average height of 450m. The rest of province is lower areas. One more noticeable fact is that 1/3 of Dak Lak’s area is Basalt, a precious type of earth allowing the province to develop the coffee, rubber, pepper, etc.
 |
| Photo: Le Bich |
Thanh Hoa (11.129,5 km2): Thanh Hoa is one of the biggest provinces in Vietnam, located 150km from Hanoi and 1,560 km from Ho Chi Minh City. This province has an important role that is being the northern tip of central Vietnam, adjacent to Son La, Hoa Binh, Ninh Binh to the north and Nghe An to the south. The province is also contiguous to the East Sea and Hua Phan Province of Laos. This position gives Thanh Hoa a crucial role in the Northern economic region of Vietnam.
Thanh Hoa has various types of terrain and can be divided into three main areas. The mountainous region, with its average height of 600-700m, is located in the west of the province. This area is approximately 839,037 ha (75.44% the total of the entire province). The second one is the plain that alternates with low mountains and hills, and the final coastal region is suitable for developing maritime industries and tourism. The weather in Thanh Hoa is tropical monsoon with four seasons and the average temperature is around 23 -24o C. The climate is also very dry with the average rainfall between 1600 and 2300mm a year, yet the high humidity rate often reaches 85%.
 |
| Photo: VnExpress |
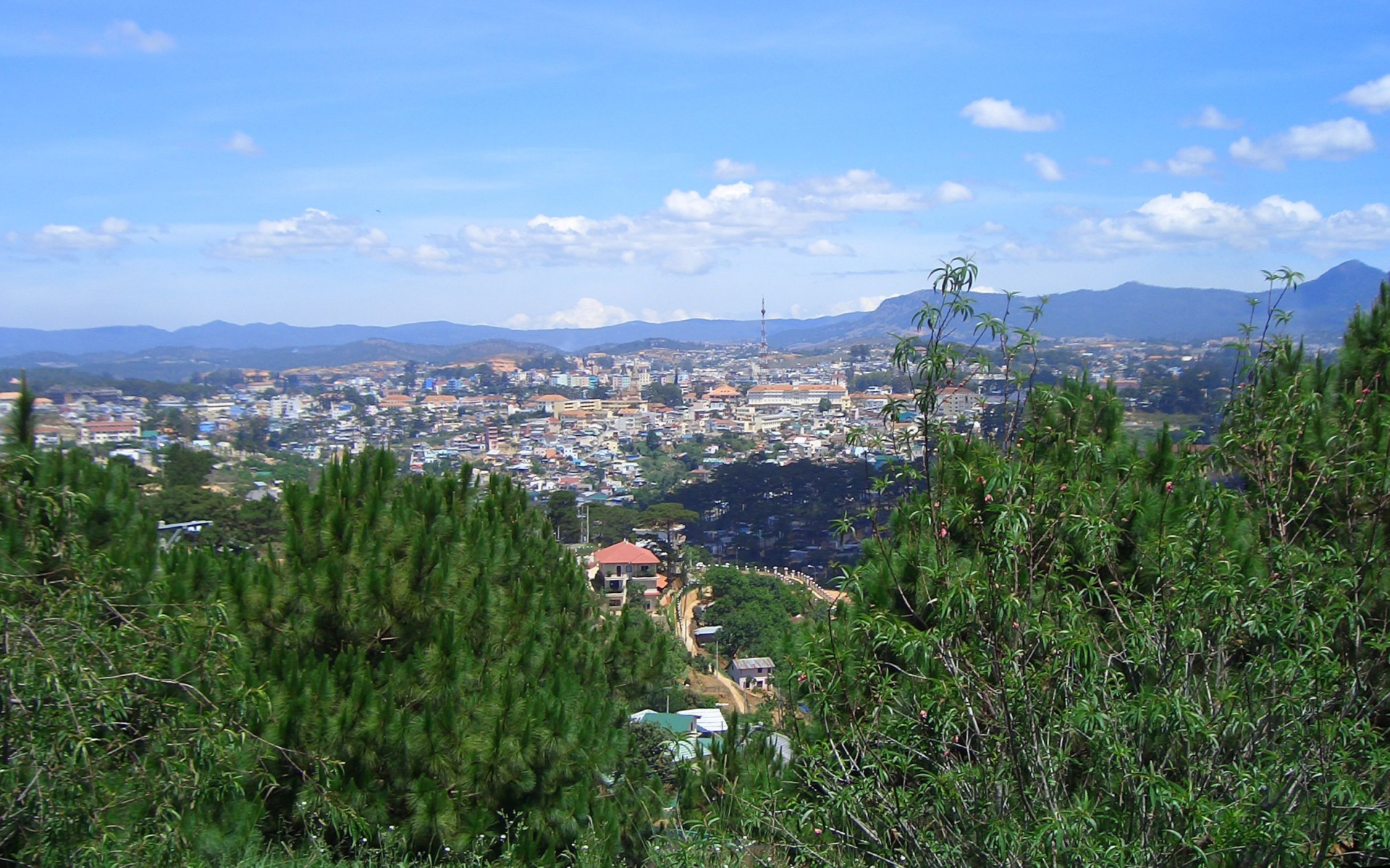
Quang Nam (10.438,4 km2): Quang Nam is a province in the Central region of Vietnam. It is bordered by Thua Thien- Hue Province to the north, the nation of Laos to the west, Kon Tum Province to the southwest, Quang Ngai Province to the southeast, the South China Sea to the east, and the city of Da Nang to the northeast. The province is known for being a tourist destination in the Hội An cultural site, alongside an export and manufacturing hub within central Vietnam.
Quang Nam has flat land along the coast and increasingly high elevations towards the west, with the highest elevations along the border to Laos and Kontum Province. The highest peak is Ngoc Linh Mountain at 2598m. In contrast to the other provinces of the South Central Coast there are no hills or mountains near the coast (with the exception of the Cham Islands with a peak at 517m).
More than half of Quang Nam’s area is covered by forests, making it one of the more forested provinces in Vietnam. Forests dominate in the west of the province and along the border to Quang Ngai Province. 111,900ha of land are used for agriculture, mostly in the east of the province.
 |
| Photo: Wikipedia |
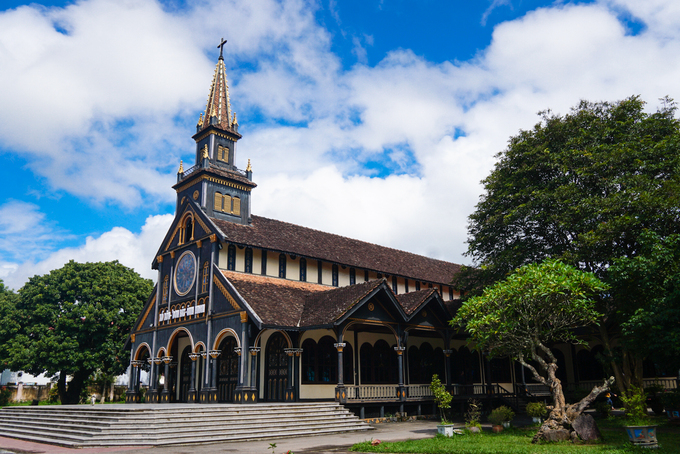
Lam Dong (9.773,5 km2): In Vietnam, Đa Lat is a popular tourist destination - highly appreciated for its temperate climate, beautiful sights such as waterfalls and lakes and its abundance of flowers and vegetables. It is the location of the Novotel Dalat (formerly Dalat Hotel) and Sofitel Dalat Palace (formerly Dalat Palace built in 1922).
Located in the Central Highlands region, Lam Dong is a mountainous province, and 70% of its area is covered in forest. To the north, it borders on Dak Lak and Dak Nong provinces, to the south-east, on Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan and Binh Thuan provinces, and to the west, on Binh Phuoc and Dong Nai provinces. The remarkable characteristic of Lam Dong's topography is the fairly distinctive division of tiers from north to south. The north of the province is high mountains, the Lang Bian plateau, with summits of altitudes between 1,300m - above 2,000m such as Bidoup (2,287m), Lang Bian (2,167m). The east and the west are mountains with modest altitudes (500m - 1,000m). The south is topographically the transition from the Di Linh - Bao Loc plateau to the semi-flat country.
Lam Dong province has a tropical climate with monsoon. On the whole territory, due to a complex topography, there is a difference in elevation and degree of vegetation covering. However, the weather of Lam Dong is temperate and mild all the year round, notable changes are rare in the annual cycle. The temperature varies distinctly between areas and the higher it is, the lower temperature is. The range of the average annual temperature is 16ºC - 23ºC. Dry season is from December to March next year. Rainy season is from April to November. It is always sunny everyday. The annual rainfall is not distributed equally in time and place. Its range is 1,600 - 2,700mm. The side of the area towards the southwest wind (Bao Loc Town) has a high annual rainfall amounting to 3,771mm.
 |
| Photo: Quynh Tran |
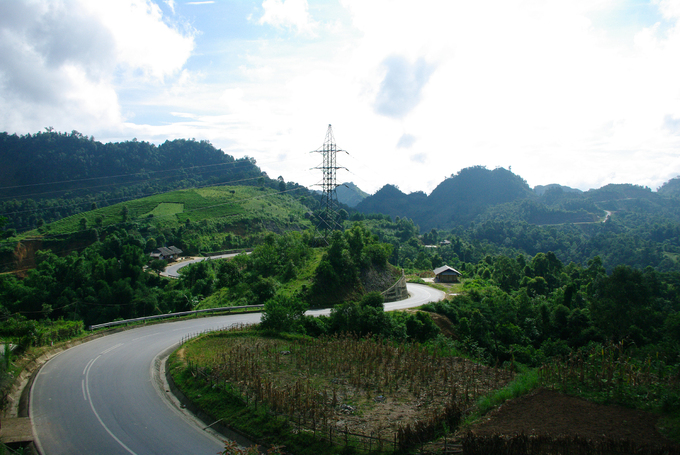
Kon Tum (9.689,6 km2): Coming to Kontum, visitors enjoy mountainous landscapes like Ngok Linh Mountain, Chu Mon Ray Primitive Forest, Dak Tre Tourist Site, and Dak To Hot Spring. Tourists are interesting in historical relics such as Kontum Former Prison, Dak Glei Prison, Ho Chi Minh Trail, Dak To, Tan Canh Battle Field.
Kon Tum is on Central Highlands. It shares border with Laos, Cambodia on the west, Quang Nam Province on the north, Quang Ngai Province on the east and Gia Lai Province on the south.
On the north, there is highest granite mountain region in Southern Vietnam with Ngok Linh 2,598m and Ngoc Phan 2,251m. It is source of Tranh, Thu Bon, Tra Khuc, Ba rivers.
Forest covers 50% total of Kon Tum area with valuable wood, rare birds. Basalt soil is suitable to plan rubber, coffee, tea, sugar cane. The province has 26,000ha grassland that gives good condition to raise cattle.
 |
| Photo: VnExpress |
Dien Bien (9.562,9 km2): Dien Bien is a province in northwestern Vietnam. It is bordered by Lai Châu and Son La provinces of Vietnam to the east and south, Pu’er City, Yunnan, China, to the north, and Phongsaly Province in Laos to the west.
Dien Bien province’s name derives from Sino-Vietnamese, meaning “stable frontier”. Dien Bien has various ancient monuments including the caves Tham Khuong, as well as Than Búa in Tuan Giáo.
In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Lu in Muong Thanh people were the most developed in the area and controlled Sìn Ho, Muong Lay, and Tuan Giáo.
In the 11th and 12th centuries, Thai people from Muong Ôm and Muong Ai occupied Muong Lò in Nghia Lo and Muong Thanh in Ðien Biên. They eventually gained control of the whole area between Muong Lò, Muong Lò, and Muong Thanh.
 |
| Photo: VnExpress |
Lai Chau (9.068,8 km2): As far as 450 kilometers from the capital, there locates a highland in northwest Vietnam, namely Lai Chau (Province). This complex of plateaus is situated at the altitude of 1,500m above sea level, comprising high mountains, pure streams and rivers. It shares borderline with Yun Nan province (China) in about 273 km to the North, Son La, Dien Bien to the west and south, and Lao Cai to the east. Accordingly, the town has a similar weather to Sapa (Lao Cai), being cool and mostly foggy all the year round, making it a visionary land in between mountains. The annual average temperature is from 21oC – 23oC, with two seasons, hot-rainy and dry-cold seasons. The whole province’s area is about 9,071 sq. Km, with a population of only 325,000 people.
Tourists coming to Lai Chau may choose between following the main road, the national 12th highway (from Dien Bien Phu town to Ma Lu Thang border gate in Lai Chau), or the 4D road (from Sapa to Lai Chau).
 | Top Beautiful Spots For Instagram "Check-in" in Vietnam As Vietnam's youth enthusiastically loves 'flexing' on Instagram, several special 'check-in' spots were created in recent years. |
 | Top 10 Most Beautiful Temples To See In Vietnam Vietnam is the land of beautiful architectures and sacred temples, where you can find peace of mind, quietness, and a better understanding of Vietnam culture. ... |
 | 8 Kinds of Banh Mi in Saigon Being in lockdown during Covid-19 pandemic can be a dreadful time, these 8 Banh Mi dishes becomes a "nostalgic" memory for Saigonese who love street ... |
Recommended
 Travel
Travel
Strategies for Sustainable Growth of Vietnam’s Tourism from International Markets
 Travel
Travel
Vietnam Strengthens Its Presence On The Global Tourism Map
 Multimedia
Multimedia
Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park Named Top Adventure Travel Site
 Travel
Travel
Phong Nha Named Top Budget-Friendly Travel Destination for Spring 2025: Agoda
Popular article
 Travel
Travel
Four Indian Films Introduced to Lao Cai Audience
 Travel
Travel
Vietnam to Waive Visas for Citizens from 12 Countries until 2028
 Travel
Travel
Ninh Binh Full-day Tour among World’s Top Experiences: TripAdvisor
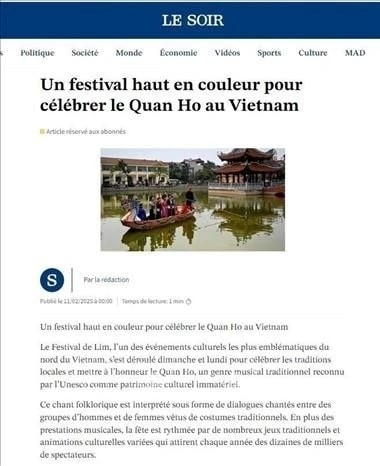 Travel
Travel










