NIH: New coronavirus can persist in air for hours and on surfaces for days
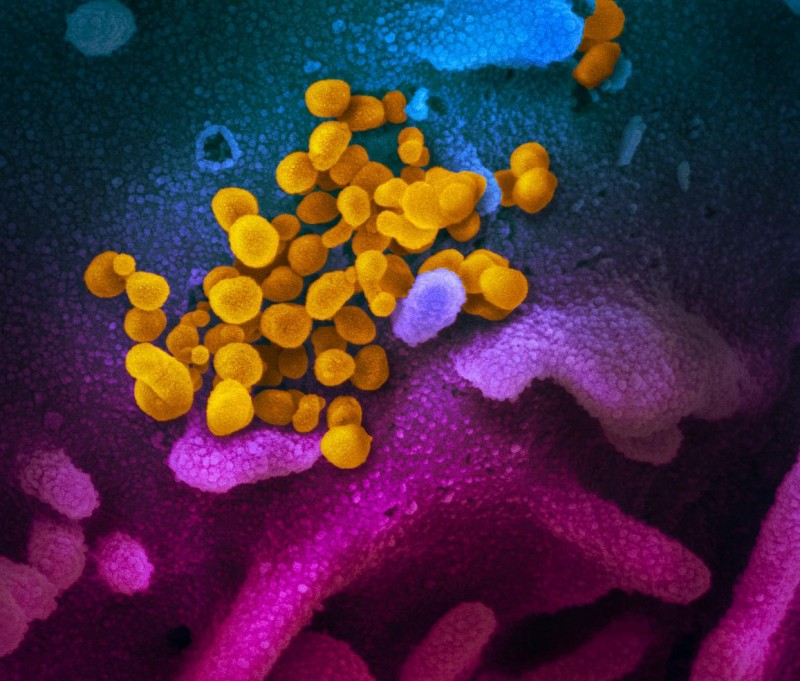 |
| This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (yellow)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells (blue/pink) cultured in the lab.NIAID-RML |
The scientists found that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in aerosols for up to three hours, up to four hours on copper, up to 24 hours on cardboard and up to two to three days on plastic and stainless steel.
The results provide key information about the stability of SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19 disease, and suggests that people may acquire the virus through the air and after touching contaminated objects. The study information was widely shared during the past two weeks after the researchers placed the contents on a preprint server to quickly share their data with colleagues.
The NIH scientists, from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases' Montana facility at Rocky Mountain Laboratories, compared how the environment affects SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. SARS-CoV-1, like its successor now circulating across the globe, emerged from China and infected more than 8,000 people in 2002 and 2003. SARS-CoV-1 was eradicated by intensive contact tracing and case isolation measures and no cases have been detected since 2004. SARS-CoV-1 is the human coronavirus most closely related to SARS-CoV-2. In the stability study the two viruses behaved similarly, which unfortunately fails to explain why COVID-19 has become a much larger outbreak.
The NIH study attempted to mimic virus being deposited from an infected person onto everyday surfaces in a household or hospital setting, such as through coughing or touching objects. The scientists then investigated how long the virus remained infectious on these surfaces.
The scientists highlighted additional observations from their study:
- If the viability of the two coronaviruses is similar, why is SARS-CoV-2 resulting in more cases? Emerging evidence suggests that people infected with SARS-CoV-2 might be spreading virus without recognizing, or prior to recognizing, symptoms. This would make disease control measures that were effective against SARS-CoV-1 less effective against its successor.
- In contrast to SARS-CoV-1, most secondary cases of virus transmission of SARS-CoV-2 appear to be occurring in community settings rather than healthcare settings. However, healthcare settings are also vulnerable to the introduction and spread of SARS-CoV-2, and the stability of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols and on surfaces likely contributes to transmission of the virus in healthcare settings.
How long does the coronavirus last on surfaces?
Droplets: The tests show that when the virus is carried by the droplets released when someone coughs or sneezes, it remains viable, or able to still infect people, in aerosols for at least three hours.
On plastic and stainless steel, viable virus could be detected after three days. On cardboard, the virus was not viable after 24 hours. On copper, it took 4 hours for the virus to become inactivated.
Aerosol droplets: In terms of half-life, the research team found that it takes about 66 minutes for half the virus particles to lose function if they are in an aerosol droplet.
That means that after another hour and six minutes, three quarters of the virus particles will be essentially inactivated but 25% will still be viable.
The amount of viable virus at the end of the third hour will be down to 12.5%, according to the research led by Neeltje van Doremalen of the NIAID’s Montana facility at Rocky Mountain Laboratories.
On stainless steel, it takes 5 hours 38 minutes for half of the virus particles to become inactive. On plastic, the half-life is 6 hours 49 minutes, researchers found.
Prevent the speard of Coronavirus
The findings affirm the guidance from public health professionals to use precautions similar to those for influenza and other respiratory viruses to prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2:
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Stay home when you are sick.
- Cover your cough or sneeze with a tissue, then throw the tissue in the trash.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces using a regular household cleaning spray or wipe.
| About the National Institutes of Health (NIH) NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov. |
-
False claim: The new coronavirus (COVID-19) is a common cold
The virus referred to in the claim is COVID-19, which is a new strain of the human coronavirus, not the general coronavirus family. The common cold is usually mild, lasts between 1-2 weeks and includes a sore throat followed by runny nose and congestion, and finally a cough ( here ). COVID-19 causes symptoms including difficulty breathing, fever and a dry cough ( here ). Some patients develop pneumonia and require hospitalization. If the pneumonia becomes more severe, it may be fatal. As of March 16, 2020 the World Health Organization (WHO) counted 6,606 deaths globally due to COVID-19 ( here ).
The World Health Organizations says: "Coronaviruses (CoV) are a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV). The most recently discovered coronavirus causes coronavirus disease COVID-19."
 | Coronavirus (covid-19) latest: Treatment and Prevention? There is no specific antiviral treatment recommended for Coronaviru (COVID-19), and no vaccine is currently available. The treatment is symptomatic, and oxygen therapy represents the ... |
 | SCMP: Honeysuckle flower can help treat flu virus Coronavirus treatment: Recently, the Hong Kong-based SCMP newspaper published an article announcing Chinese scientists’ work showing that traditional medicines, including Jin Yin Hua (honeysuckle flower), ... |
 | Covid-19 patients in Vietnam receive Free Treatment In Vietnam, Covid-19 patients will be exempted from the full treatment fee. Negative case's testing costs are paid by Health Insurance. |
 | 'False hope’ to think COVID-19 will disappear on summer, high temperatures? Head of WHO’s health emergencies programme says it is ‘a false hope’ to think Coronavirus (COVID-19) will just disappear like the flu when the seasons ... |
In topics
Recommended
 World
World
India reports 9 Pakistani Aircraft Destroyed In Operation Sindoor Strikes
 World
World
Thailand Positions Itself As a Global Wellness Destination
 World
World
Indonesia Accelerates Procedures to Join OECD
 World
World
South Korea elects Lee Jae-myung president
Popular article
 World
World
22nd Shangri-La Dialogue: Japan, Philippines boost defence cooperation
 World
World
Pakistan NCRC report explores emerging child rights issues
 World
World
"India has right to defend herself against terror," says German Foreign Minister, endorses Op Sindoor
 World
World