Clarification of Governmental Directive 15 and Directive 16 on Covid-19 preventation
| Nearly $ 21.3 million raised from Vietnam governmental bond auction | |
| PMs: Vietnam – Laos Inter-Governmental Committee meeting a success | |
| More than 500 foreign NGOs operate regularly in Vietnam |
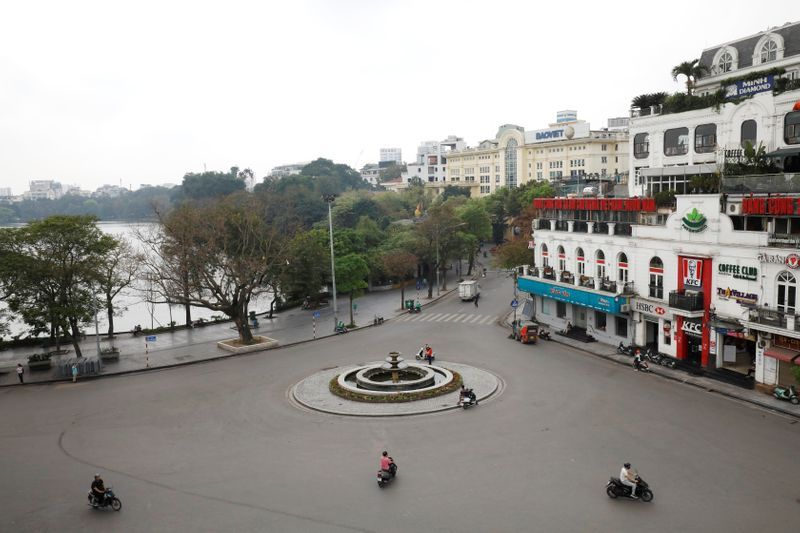 |
| Dong Kinh Nghia Thuc square is seen almost empty during the social distancing for Covid-19 preventation in Hanoi, Vietnam. Photo: REUTERS |
Viet Nam has gone a week without new a COVID-19 infection cases, keeping the nation’s patient tally at 268, Hanoi and Hochiminh City have been allowed to end their social distancing campaigns under the prime ministerial Directive No 16 on Thursday.
On Wednesday April 22 afternoon, Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc agreed to classify Hanoi as one of local groups of "at risk" epidemic spread with some activity easing. However, some districts having less than 14 day infections include Thuong Tin, Me Linh and others still considered "high risk" areas.
"High-risk" areas continue strictly being imposed the Prime Minister's Directive 16 on social distancing. Hanoi People's Committee Chairman has decided to put an social distancing implementation on these places.
The Vietnamese government issued the Prime Minister’s Directive No 15 on March 27 and extended it April 15 on maximum social distancing, which had been set to expire. The Vietnamese government has categorized localities based on perceived risk, with those designated as lower risk (mostly rural areas and smaller cities) able to relax social distancing restrictions sooner. High-risk localities (including Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, and Danang) are all expected to continue Directive 16’s social distancing efforts until April 22, with a potential extension until April 30 depending on the developing COVID-19 situation. Localities considered to be medium-risk must follow Directive 16 until April 22. Localities designated in the lowest risk category will follow Directive 15, which has less restrictive social distancing requirements
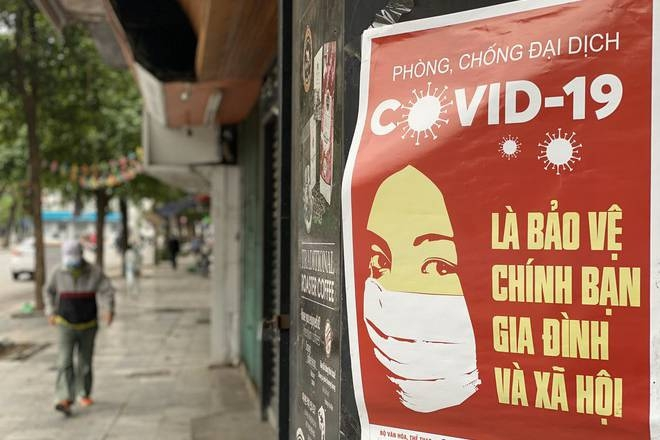 |
| It is important for people to obey PM's Directives in order to prevent and control the pandemic effectively. |
Let's clarify the differences between Directive No 15 and Directive No 16
Directive 15 issued on March 27, requesting the provincial People Committee to impose limited measures of public crowds; meeting activities, 20 people gathering events; and do not gather from 10 people up outside the workplaces, schools, hospitals. a minimum 2m distance is required between individuals in public places. Religious or belief establishments must suspend all religious rituals and activities of 20 people up. Service-providing establishments in their localities, except for those dealing in essential goods and services, must temporarily cease their operations. Chairmen of the provincial / municipal People Committees are competent to decide on businesses and services need closing or suspending. The Directive 15 does not require social distancing.
Directive 16 issued on March 31, concerning the implementation of urgent solutions to prevent and combat COVID-19. Accordingly, the Government leader ordered a 15-day period of nationwide isolation starting 00:00 on April 1, with the principle of every household, village, commune, district and province going into self-isolation but not lockdowns. So, the Directive 16 requires social distancing nationwide. Any citizen required to stay home, only go out for necessities such as food and medicine purchasing or emergency; or working at factories, production facilities, essential goods and service providers (uninterruptible places) and other emergencies. All people must seriously implement the minimum 2m distance in their communication. It also puts a ban on more than 2 people concentration outside the workplaces, schools, hospitals and in public places.
In the 22-day distancing campaign for "high-risk" localities ending Wednesday April 22, all "non-essential" businesses such as bars, clubs, karaoke, massage services... were ordered to close temporarily.
Vietnam’s confirmed 268 Covid-19 cases so far, 223 have recovered and no deaths. The country has recorded no new infection in the last six days.
 | Government gradually loosens COVID-19 control measures from April 22 When Vietnam records the COVID-19 situation getting better, Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc said it is necessary to gradually loosen containment measures and the decree of ... |
 | Hanoi students may return their shools in first half of May Hanoi People Committee Vice President Ngo Van Quy in the Covid-19 preventation meeting by Hanoi steering committee on Monday afternoon April 20 said that the ... |
 | Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City propose to ease social distancing order Vietnam’s two largest cities have proposed to the government to not extend the social distancing order after April 22 to return the normal life as COVID-19 ... |
Recommended
 National
National
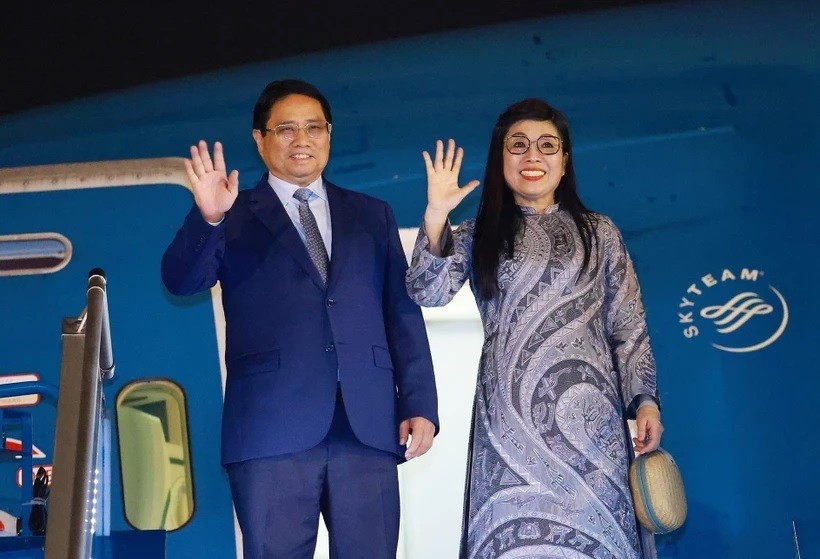
Vietnam News Today (Jun. 5): PM sets off for attendance at UNOC 3 in France, official visits to Estonia, Sweden
 National
National
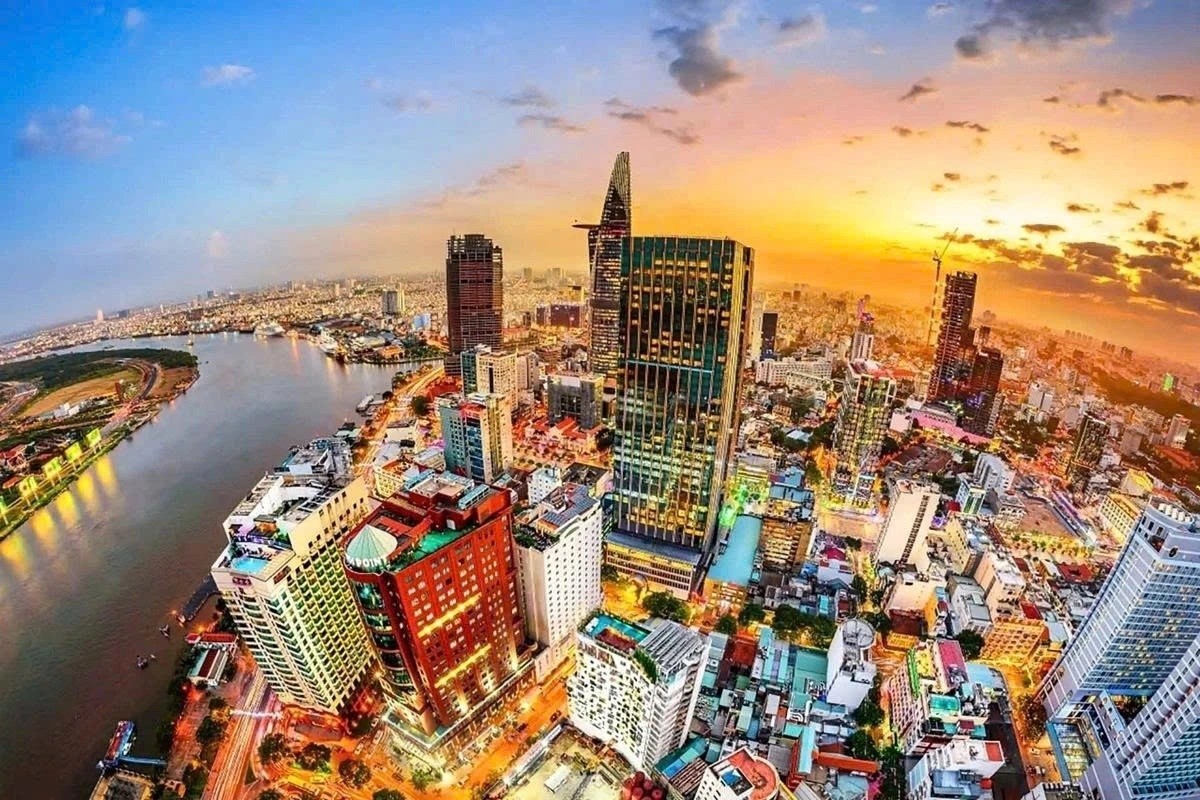
Vietnam News Today (Jun. 4): Vietnam - Promising Candidate for Southeast Asia’s Next Powerhouse
 National
National
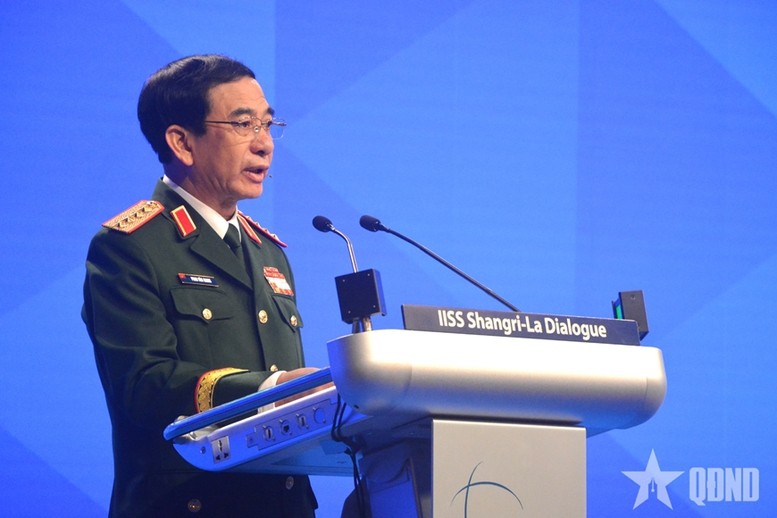
Shangri-La Dialogue 22: Vietnam Highlights Some Issues of Ensuring Stability in a Competitive World
 National
National
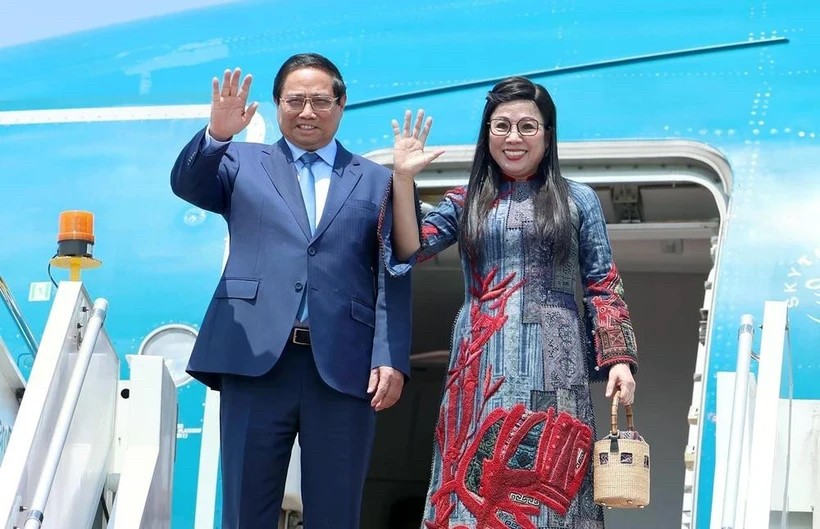
Vietnam News Today (Jun. 3): PM Pham Minh Chinh to Attend UN Ocean Conference, Visit Estonia, Sweden
 National
National
Vietnam News Today (Jun. 2): Vietnamese Trade Mission Sounds Out Business Opportunities in United States
 National
National
Vietnam News Today (Jun. 1): Vietnamese, Japanese Firms Foster Partnership
 National
National
Vietnam News Today (May 31): Vietnam Strongly Supports Laos’s National Development
 National
National