The Biggest Tech Trends of 2022
Global spending on digital transformation is predicted to jump 20 per cent annually to $1.8 trillion next year, according to Statista.
Covid-induced market disruptions and widespread adoption of hybrid work models have accelerated the process. Many businesses are more inclined towards developing in-house technologies to reduce their dependence on third-party service providers and ensure they are less affected in case of future supply chain disruptions, industry experts said.
“Digital tech initiatives remain a top strategic business priority for companies as they continue to reinvent the future of work … focusing spending on making their infrastructure bulletproof and accommodating increasingly complex hybrid work for employees going into 2022,” said Jon-David Lovelock, research vice president at Gartner.
Take a look at these best technology trends that are coming in 2022.
Why is technology trend awareness important
Regardless of which industry we fall under or which department we work under, keeping up with the technology trends is imperative. Following are the areas where technology trend awareness skills play their significant role:
- Enhancing your visibility to the customers. According to an estimate, more than 2 billion people use their mobile devices for internet access. Technology has been absorbed in everyone’s lives to the extent that every day we all interact with one kind of screen or another, mostly using internet. Therefore, your customers could be anywhere using any kind of technology. Technology trend awareness helps you identify what your customers are mostly spending their time with so that you can connect with them easily. For instance, if it’s their mobile devices they prefer to use, have you pondered over how your website looks in mobile format?
- Increasing opportunities with new ideas and new ventures. Technology trend awareness doesn’t necessarily help with marketing alone. It increases opportunities to improve other areas as well. ‘Lean manufacturing’ is a good example of improvements through technology trend awareness skills. you can adopt new and trending technologies without necessarily having a technology-centric business, or start a new technology-centric venture, all for the sake of additional revenue opportunities.
1. Generative artificial intelligence
 |
| Photo: Avenga |
Generative AI is a new buzzword that emerged with its novel applications like DeepFake. Generative AI leverages AI and machine learning algorithms to enable machines to generate artificial content such as text, images, audio and video content based on its training data, in a manner which tricks the user into believing the content is real. However, generative AI faces certain challenges concerning data privacy and use in fraudulent or criminal acts.
Identity Protection: Generative AI avatars provide protection for people who do not want to disclose their identities while interviewing or working.
Robotics control: Generative modeling helps reinforcement machine learning models to be less biased and comprehend more abstract concepts in simulation and the real world.
Healthcare: Generative AI enables early identification of potential malice to create effective treatments. For example, GANs compute different angles of an x-ray image to visualize the possible expansion of the tumor.
What are the challenges of Generative AI?
Security: Some people can use Generative AI for fraudulent purposes like scamming people.
Overestimation of capabilities: Generative AI algorithms require an enormous amount of training data to perform tasks. Yet, GANs cannot create entirely new images or texts. They only combine what they know in different ways.
Unexpected outcomes: In some models of Generative AI like GANs, it is not easy to control their behavior. They perform unstably and generate an unexpected outcome.
Data privacy: Health-related applications involve privacy concerns on individual-level data.
2. The chip shortage
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
The 2020–2022 global chip shortage is an ongoing crisis in which the demand for integrated circuits (commonly known as semiconductor chips) is greater than the supply, affecting more than 169 industries and has led to major price increases, shortages and queues amongst consumers for cars, graphics cards, video game consoles, computers, and other products that require semiconductors. Commonly cited causes for the shortage include the COVID-19 pandemic, the China–United States trade war, and various severe weather incidents.
While the U.S. leads the world in developing and selling semiconductors, accounting for 45% to 50% of global billings, manufacturing has shifted to Asia. Taiwan and Korea account for 83% of global processor chip production and 70% of memory chip output, and the region's lead is projected to continue to expand.
Taiwan dominates the foundry market, especially Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., which is more commonly known as TSMC and accounted for 54% of total global foundry revenue last year.
There wasn't always a shortage. Worldwide semiconductor sales declined between 2018 and 2019, but by 2020, sales grew 6.5%, according to trade organization the Semiconductor Industry Association. The rapid growth continued into 2021, and sales in the third quarter of 2021 were 27% higher than the same time period last year. More semiconductor units were shipped during the third quarter of 2021 than during any other quarter in the market's history, the SIA said.
3. Autonomic systems
As businesses continue to transform, traditional programming or simple automation will not scale enough.
Autonomic systems are self-managing physical or software systems that learn from their environments. Unlike automated or even autonomous systems, autonomic systems can modify their own algorithms without an external software update, enabling them to rapidly adapt to new conditions in the field, much like humans can.
“Autonomic behaviour has already made itself known through recent deployments in complex security environments, but in the longer term will become common in physical systems such as robots, drones, manufacturing machines and smart spaces,” said David Groombridge, research vice president at Gartner.
4. Quantum computing
 |
| Photo: CNET |
Quantum computing is a type of computation that harnesses the collective properties of quantum states, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement, to perform calculations. The devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers are too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, they are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science.
There are several types of quantum computers (also known as quantum computing systems), including the quantum circuit model, quantum Turing machine, adiabatic quantum computer, one-way quantum computer, and various quantum cellular automata. The most widely used model is the quantum circuit, based on the quantum bit, or "qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 quantum state, or in a superposition of the 1 and 0 states. When it is measured, however, it is always 0 or 1; the probability of either outcome depends on the qubit's quantum state immediately prior to measurement.
Efforts towards building a physical quantum computer focus on technologies such as transmons, ion traps and topological quantum computers, which aim to create high-quality qubits. These qubits may be designed differently, depending on the full quantum computer's computing model, whether quantum logic gates, quantum annealing, or adiabatic quantum computation. There are currently a number of significant obstacles to constructing useful quantum computers. It is particularly difficult to maintain qubits' quantum states, as they suffer from quantum decoherence and state fidelity. Quantum computers therefore require error correction.
5. Blockchain: Ready for business
 |
| Photo: Forbes |
Trendy cryptocurrencies and nonfungible tokens capture media headlines and the public imagination, but these and other blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) are also making waves in the enterprise. In fact, blockchain and DLT platforms have crossed the disillusionment trough of the hype cycle and are well on their way to driving real productivity. They are fundamentally changing the nature of doing business across organizational boundaries and helping companies reimagine how they make and manage identity, data, brand, provenance, professional certifications, copyrights, and other tangible and digital assets. Emerging technical advancements and regulatory standards, especially in nonpublic networks and platforms, are helping drive enterprise adoption beyond financial services organizations. As enterprises get comfortable with blockchain and DLT, creative use cases are cropping up in many industries, with established industry leaders expanding their portfolios and creating new value streams, while startups dream up exciting new business models.
6. Data-sharing made easy
 |
| Photo: Smart Factory & Industrial IoT Vietnam |
A host of new technologies promise to simplify the mechanics of data-sharing across and between organizations while preserving the veil of privacy. As part of a growing trend, organizations are unlocking more value from their own sensitive data while leveraging enormous volumes of externally sourced data that has traditionally been off limits. This can open up a new arena of data-driven opportunities. Indeed, the ability to share secured data with others within an ecosystem or value chain is giving rise to new business models and products. For example, by pooling clinical data on shared platforms in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers, medical authorities, and drug makers were able to accelerate the development of treatments and vaccines. Moreover, these same data-sharing protocols have helped drug makers, government agencies, hospitals, and pharmacies coordinate and execute expansive vaccination programs that prioritize efficiency and safety, and preserve intellectual property.
7. Hyperautomation
 |
| Photo: Shutterstock |
It’s the extension of legacy business process automation beyond the confines of individual processes. By marrying AI tools with RPA, hyperautomation enables automation for virtually any repetitive task executed by business users.
It even takes it to the next level and automates the automation - dynamically discovering business processes and creating bots to automate them. Hyperautomation was identified by Gartner as one of the year’s top 10 strategic technology trends.
With a range of tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI), working in harmony to automate complex business processes—including where subject matter experts were once required—hyperautomation is a means for real digital transformation.
According to Gartner, RPA enriched by AI and ML becomes the core enabling technology of hyperautomation. Combining RPA and AI technologies offers the power and flexibility to automate where automation was never possible before: undocumented processes that rely on unstructured data inputs.
8. Cyber security mesh
 |
| Photo: Information Age |
Cybersecurity mesh is a cyber defense strategy that independently secures each device with its own perimeter — such as firewalls and network protection tools. Many security practices use a single perimeter to secure an entire IT environment, but a cybersecurity mesh uses a holistic approach.
Developing the concept of cybersecurity mesh may be a much-needed revolution, ensuring sensitive data safety in times of intensified remote work. Cybersecurity Mesh is a broader concept that involves a wider network of nodes. More specifically, a Cybersecurity Mesh consists in designing and implementing an IT security infrastructure that does not focus on building a single ‘perimeter’ around all devices or nodes of an IT network, but instead establishes smaller, individual perimeters around each device or access point. This creates a modular and more responsive security architecture covering physically disparate access points of the network.
 | Vietnam Striving to Master Technology in Renewable Energy The draft Power Development Planning (PDP) VIII has demonstrated the trend of developing clean and renewable energy in line with commitments to cutting carbon emissions ... |
 | Vietnam-Germany Innovation Network Bolsters Cooperation in Science-technology The Vietnam-Germany Innovation Network (VGI) and the Bach Khoa Hanoi Technology Investment and Development One Member Company Limited (BK-HOLDINGS) inked an agreement on enhancing cooperation ... |
 | Best Tech Gadgets for Christmas Gifts All of these fantastic products, from folding phones, headphones, and VR headsets to smart speakers and eco-friendly phone cases, are outstanding, built to last, and ... |
Recommended
 Handbook
Handbook
Vietnam Moves Up 8 Places In World Happiness Index
 Handbook
Handbook
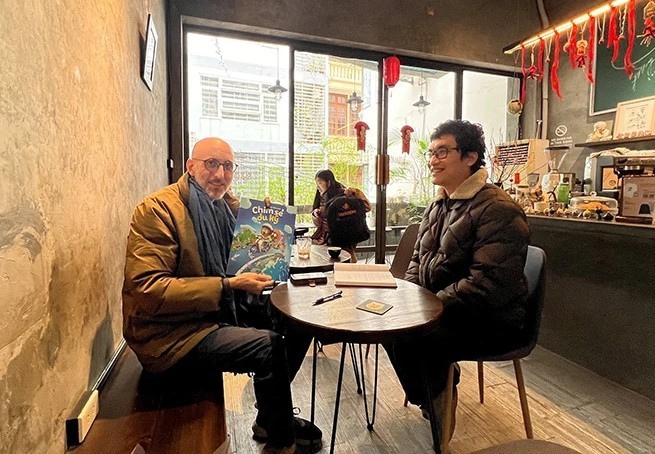
Travelling Vietnam Through French Artist's Children Book
 Multimedia
Multimedia
Vietnamese Turmeric Fish among Best Asian Dishes: TasteAtlas
 Handbook
Handbook
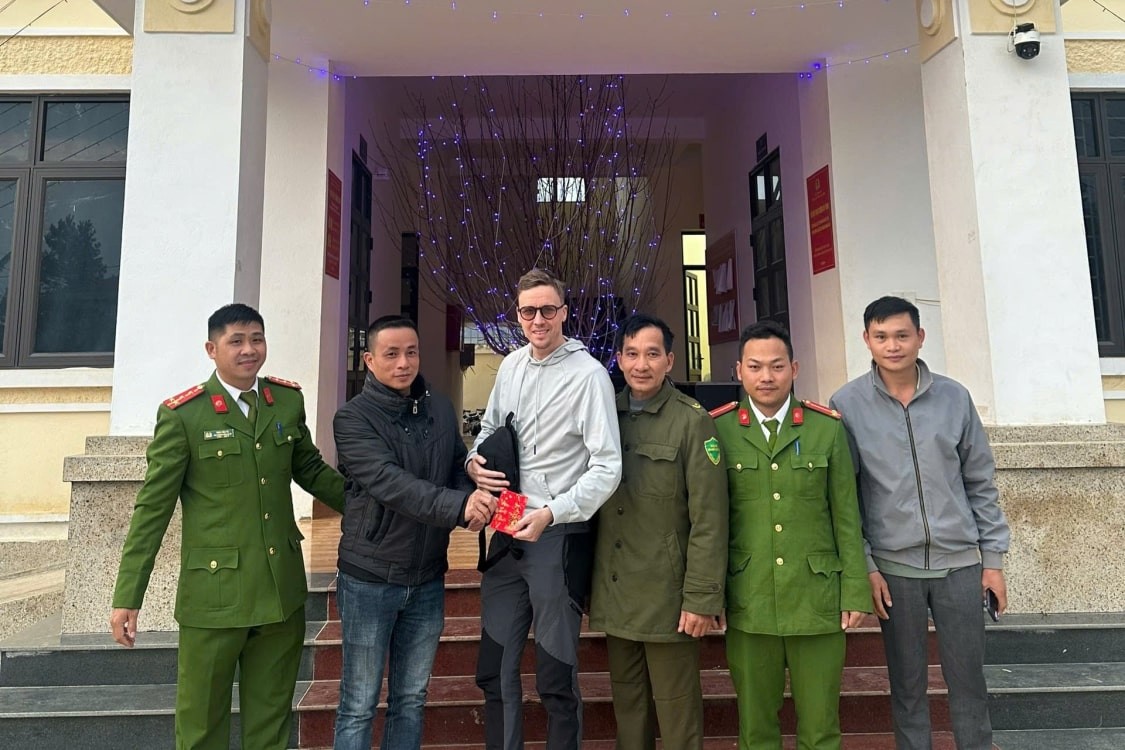
From Lost to Found: German Tourist Thanks Vietnamese Police for Returning His Bag
Popular article
 Handbook
Handbook
Prediction and Resolution for the Disasters of Humanity
 Handbook
Handbook
16 French Films To Be Shown For Free During Tet Holiday In Vietnam
 Handbook
Handbook
Unique Cultural and Religious Activities to Welcome Year of the Snake
 Handbook
Handbook







