WHO accused of conspiring with Italy to cover mismanagement of COVID-19
 |
| Italian doctors treating a Covid-19 patient (Photo: AP) |
As reported by The Guardian, Italy was the first European country to become engulfed by the pandemic. The report, produced by the WHO scientist Francesco Zambon and 10 colleagues across Europe, was funded by Kuwait’s government with the objective of providing information to countries yet to be hit.
Italy’s First Response to Covid-19, the document was published on the WHO website on 13 May before being taken down the next day, as first reported by the Guardian in August. The 102-page reportsaid Italy’s pandemic plan had not been updated since 2006 and that, due to being unprepared, the initial response from hospitals was “improvised, chaotic and creative”. It took time for formal guidance to become available, the report added.
| The document was allegedly removed at the request of Ranieri Guerra, the WHO’s assistant director general for strategic initiatives. Guerra was the director general for preventive health at the Italian health ministry between 2014 and late 2017, and was therefore responsible for updating the pandemic plan as per new guidelines laid out by the WHO and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Guerra is among the scientists on the Italian government’s Covid-19 taskforce. The outdated plan is a crucial element in the preliminary investigations being carried out by prosecutors in Bergamo – the Lombardy province hardest hit during the first wave of the pandemic – into possible criminal negligence by authorities. Covid-related deaths in Italy surpassed 60,000 on Sunday, the highest toll in mainland Europe. |
Investigators are also using a report compiled after the first wave by a retired army general, Pier Paolo Lunelli, which concluded that as many as 10,000 deaths may have been attributed to the lack of sufficient anti-pandemic protocols.
Zambon, who is based at the WHO’s office in Venice, has been summoned three times to speak to prosecutors but has been prevented from doing so by the WHO, which has insisted he and the other 10 researchers involved in producing the report should have immunity from testifying. Only Guerra was heard by prosecutors in early November but the contents of the hearing have not been disclosed.
After the first summons to Zambon and the other researchers was issued, the WHO said the regional prosecutors needed to follow diplomatic channels by making their request via Italy’s foreign ministry.
Zambon’s latest summons was on 10 December, but again he was blocked from going despite requesting permission.
“When I received the first summons I reported it to the WHO’s legal office and soon after they responded saying I couldn’t go as I was protected by immunity, despite the fact that I wanted to go as I had something to say,” Zambon told the Guardian.
Zambon claims Guerra threatened him with job dismissal unless he modified the part of the text referring to the outdated plan. He said that despite informing senior WHO officials of the threats and risks posed to the organisation’s transparency and neutrality, no internal inquiry was carried out. At the time, the WHO did not explain why the report was removed but said in a statement last week that it “contained inaccuracies and inconsistencies”.
“The report did not criticise the Italian government but highlighted the criticalities faced in the management of the pandemic, starting from the premise of the old pandemic plan, which was only ‘reconfirmed’ and not updated in 2017,” Zambon said. “The team thoroughly checked this and found that all the plans that came after 2006 were just copied and pasted – not a word or comma was changed in the text.”
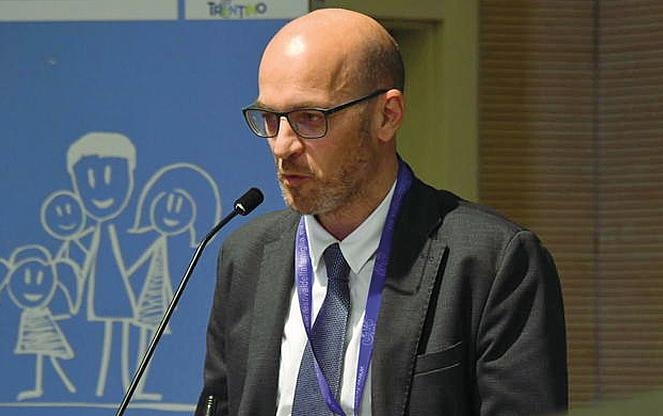 |
| Francesco Zambon (Photo: Noi Denunceremo) |
Zambon claims that a month before publication he sent an outline of the findings to Guerra, who shared it with Italy’s health minister, Roberto Speranza.
Emails sent in May to Zambon by Guerra and Hans Kluge, the WHO’s Europe director – who also wrote the introduction of the removed document – also appear to reflect a pact made with the Italian health ministry to keep the report under wraps. The emails, seen by the Guardian, formed part of a recent documentary by Report, an investigative programme on the state TV channel, Rai.
In one dated 13 May, Guerra wrote: “If even the WHO criticises without an agreement the political sensibility of the [health] minister … I do not think we are doing a great service to the country.” Guerra then tells Zambon “not to forget” that “they have just given us 10m as a voluntary contribution on the basis of trust and as an acknowledgment of what we have done so far … after six years with nothing.” Kluge’s email to Zambon on 15 May begins: “But it dos [sic] not take away a key issue: my relation with the minister who was very disappointed.”
Kluge ends the email by saying he will write to the [health] minister to establish an expert group between the WHO, Italy’s health ministry and higher health institute to review the document. “Kuwait is happy, now we need MoH happy …”
The WHO said in an emailed statement to the Guardian on Thursday: “We are currently working with the Italian government to clear up the issue.” Referring to the removed document, the statement added: “While it was offline, a decision was taken to instead use a new mechanism created in the early months of the pandemic aimed at helping member states conduct intra-action reviews and assess their Covid-19 responses; follow best practices; prevent errors; and update national strategic preparedness and response plans. The document was, therefore, not republished.
“We understand that the issuance and subsequent removal of the report caused confusion and we have updated our publishing procedures accordingly.”
Italy’s health ministry denied any involvement: “As far as we know, this is not an official WHO document and has never been sent to the ministry of health, which therefore has never assessed or commented on it. Any information pertaining to it does not come from institutional sources,” it said in a statement. Speranza recently said in an interview that the WHO “should be reformed and strengthened in order to increase transparency”.
 |
| Medical workers treat a patient in the Brescia Poliambulanza hospital in Lombardy, the province hardest hit during the first wave of the pandemic (Photo: AFP) |
As of Thursday night, Guerra had not replied to a request for comment.
If Bergamo prosecutors find that Italy had failed to update its pandemic plan, then all health ministers and prime ministers since 2013 risk facing trial. Antonio Chiappani, the chief prosecutor, told Corriere della Sera this week: “Italy was unprepared for Covid, there was a lot of improvisation … we need to find out why there are so many victims compared to elsewhere.”
Zambon said the information contained in his report could have helped save lives in countries that were behind the pandemic curve.
“I desperately wrote to all senior officials, including the director general, warning about the danger [of the report being blocked],” he said. “Its publication had life-saving potential and the accountability and liability of the WHO was at stake, because a personal conflict of interest was considered more important than sharing lessons learned from the hardest-hit country at that moment.”
Luigi Di Maio, Italy’s foreign minister, sent out a strong signal to the WHO this week when he said he was “against immunities”. The WHO said in its statement that Guerra had spoken to prosecutors “in his personal capacity”. The statement added: “WHO (and UN) staff are international civil servants who undertake all activities impartially and without fear of retribution or expectation of favour. To preserve its objectivity and independence, WHO does not normally become involved in legal matters at the national level.”
Zambon did not receive a formal refusal from the WHO preventing him from speaking to prosecutors on 10 December, but was informed on Wednesday night that the WHO had written to Italy’s foreign ministry, saying: “Zambon and other aforementioned WHO experts have been requested not to present themselves at these hearings.”
Zambon said he was ready to collaborate with prosecutors, who have so far interviewed the prime minister, Giuseppe Conte, and Speranza. He added that the reference to the report being “full of inaccuracies” was defamatory and that it had gone through all the required stages of checks.
“It’s not about the consequences that I might suffer,” Zambon said. “I do this because I strongly believe that the world needs a transparent and independent WHO, which ultimately focuses on the people.”
Current COVID-19 situation in Italy
Italy is reclaiming a record that nobody wants — the most coronavirus deaths in Europe — after the health care system again failed to protect the elderly and government authorities delayed imposing new restrictions, according to AP.
Italy added 649 more victims Saturday, bringing its official total to 64,036. According to the official British government total of 64,024, Italy did overtake Britain, though the Johns Hopkins University tally late Saturday still showed Britain leading Europe with 64,123 dead. Both numbers are believed to greatly underestimate the real toll, due to missed infections, limited testing and different counting criteria.
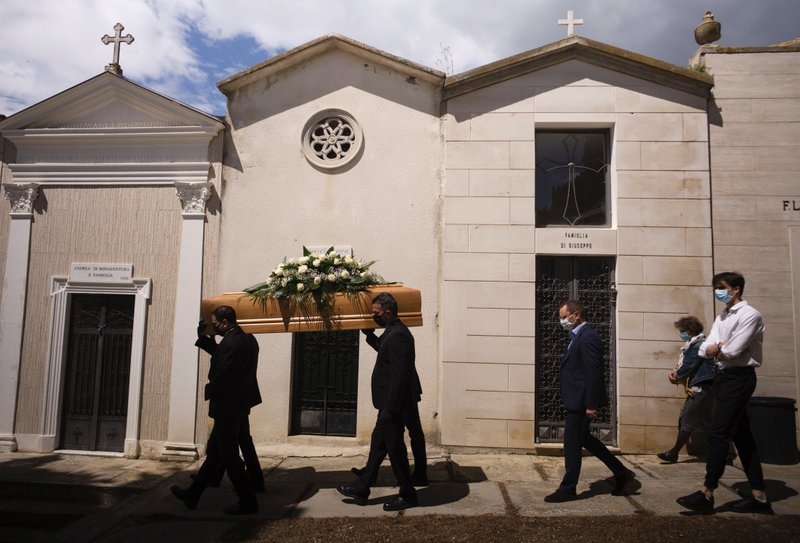 |
| Italians carrying the casket of a COVID-19 victim (Photo: AP) |
Italy is taking over the dishonorable ranking despite having 6 million people fewer than the U.K.’s 66 million, to trail only the much larger U.S., Brazil, India and Mexico. According to the Hopkins tally, Italy has the most deaths per 100,000 population among the most affected countries.
With another wave of infections feared to be just around the corner with Christmas visits and the winter flu season, many are wondering how many more will die.
 | COVID-19 Updates (Dec. 12): Vietnam’s trade surplus hits record despite COVID-19 In the first 11 months of 2020, Vietnam posted a record trade surplus of 20.1 billion USD despite the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic. |
 | Vietnam to roll out nasal spray and eye-drop COVID-19 vaccine Along with injections, Vietnam’s COVID-19 Nanocovax vaccine will also be developed in the form of eye-drop and nasal spray for special subjects. |
 | JICA President pays the first overseas visit from the Covid-19 outbreak to Vietnam On December 9, President of the Japan International Cooperation Agency Kitaoka Shinichi paid his first overseas business trip visit to the Socialist Republic of Vietnam ... |
Recommended
 World
World
India strikes back at terrorists with Operation Sindoor
 World
World
India sending Holy Relics of Lord Buddha to Vietnam a special gesture, has generated tremendous spiritual faith: Kiren Rijiju
 World
World
Why the India-US Sonobuoy Co-Production Agreement Matters
 World
World
Vietnam’s 50-year Reunification Celebration Garners Argentine Press’s Attention
Popular article
 World
World
"Will continue offering our full support to Indian govt": US FBI Director after Pahalgam attack
 World
World
"Great Leader": JD Vance Lauds PM Modi During His India Visit
 World
World
Trump’s Tariff Pause: A Strategic Move from “The Art of the Deal”?
 World
World