Construction On World's First Commercial Modular Small Reactor Starts In China
| China vows to defend Sino-Iran ties, safeguard nuclear deal | |
| China's fourth aircraft carrier likely to be nuclear powered, sources say | |
| Vietnam weighs return to nuclear energy post 2035 |
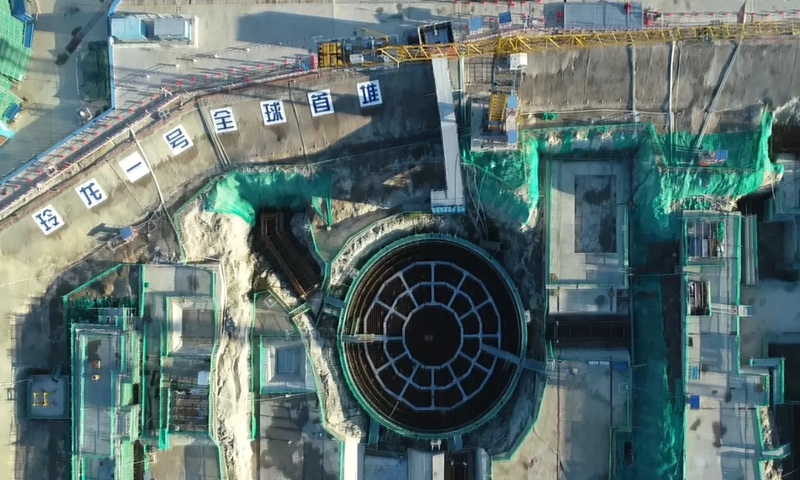 |
| The Linglong 1. Photo: CNNC |
China has started construction of the first commercial onshore nuclear project using its homegrown "Linglong One" small modular reactor (SMR) design, the China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) said on July 13, about four years later than planned.
CNNC originally aimed to start building the project at the Changjiang nuclear reactor complex on the island province of Hainan in 2017, but it has been subject to regulatory delays, according to Reuters.
The "Linglong One", also known as the ACP100, was the first SMR to be approved by the International Atomic Energy Agency in 2016. Each unit has power generating capacity of 125 megawatts (MW).
It was designed to complement the state-run CNNC's larger third-generation 1,170-MW "Hualong One" reactors, which China is planning to roll out rapidly at home and promote overseas.
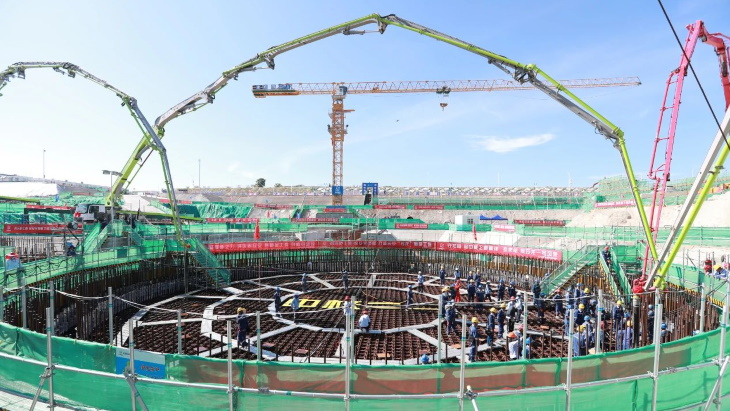 |
| First concrete being poured for the basemat of the ACP100 demonstration plant at Changjiang. Photo: CNNC |
SMRs are cheaper and quicker to build than traditional reactors, and can also be deployed in remote regions and on ships and aircraft. Their "modular" format means they can be shipped by container from the factory and installed relatively quickly on any proposed site.
China has been looking into using small reactors to provide urban heating in the north and run desalination facilities along the coast. It is also using them to support construction activities in disputed parts of the South China Sea (Bien Dong Sea).
Global Time said that unlike 3rd-generation large reactors such as the Hualong 1, which has an electric power output of 1 million kilowatts, far greater than the power range of a small reactor, the Linglong 1 can realize the multi purposes of nuclear energy, such as heat supply for cities, industrial steam, seawater desalination, oil exploitation and other different needs, in addition to electricity generating.
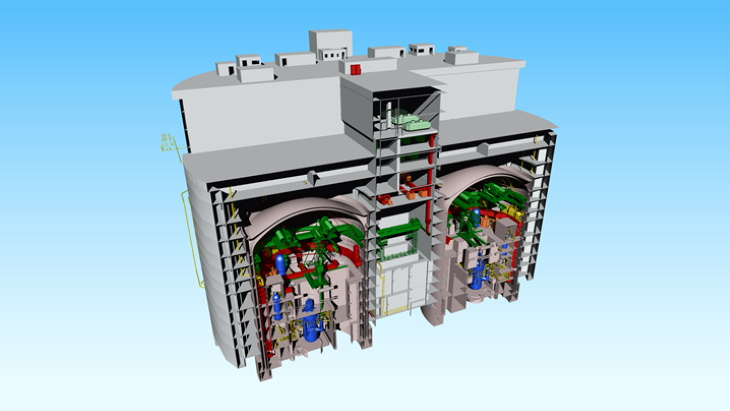 |
| A cutaway of a plant based on two ACP100 reactors. Photo: CNNC |
The energy generated by Linglong 1 can be applied to various scenarios such as industrial parks, islands, mining areas and energy supplied by high-energy consuming enterprises, meeting the development needs of Hainan.
At present, CNNC has built China's southernmost nuclear power base in Hainan, and put into operation a number of power projects, including the Changjiang Nuclear Power Plant, which has reversed the chronic shortage of power.
The popularization and application of the commercial modular small reactor on land can greatly reduce the consumption of fossil energy in China and promote energy conservation and carbon emission reduction, the company said.
By the end of June this year, China has built a total of 51 nuclear power units, including 19 nuclear power units under construction, including the small reactor projects started on July 13./.
 | US Rejects China Maritime Claims In South China Sea (Bien Dong Sea) The United States rejects China's "unlawful" maritime claims in the South China Sea (known as Bien Dong Sea in Vietnam) and stands with Southeast Asian ... |
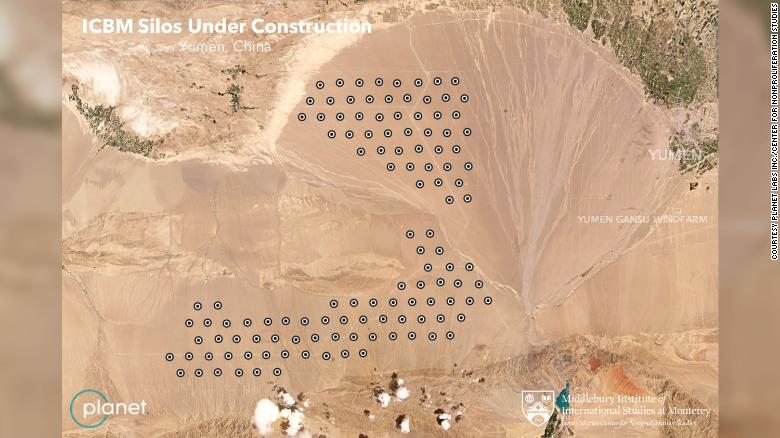 | China building sprawling network of missile silos, satellite imagery shows Researchers have warned China may be expanding its nuclear capabilities after satellite images indicated more than 100 missile silos were being built in the the ... |
 | China operating world’s second-biggest hydropower dam raising environmental concerns The first two generating units of the world’s second-biggest hydroelectric dam were officially turned on Monday in southwestern China, and also raising environmental concerns. |
Recommended
 World
World
Nifty, Sensex jumped more than 2% in opening as India-Pakistan tensions ease
 World
World
Easing of US-China Tariffs: Markets React Positively, Experts Remain Cautious
 World
World
India strikes back at terrorists with Operation Sindoor
 World
World
India sending Holy Relics of Lord Buddha to Vietnam a special gesture, has generated tremendous spiritual faith: Kiren Rijiju
 World
World
Why the India-US Sonobuoy Co-Production Agreement Matters
 World
World
Vietnam’s 50-year Reunification Celebration Garners Argentine Press’s Attention
 World
World
"Will continue offering our full support to Indian govt": US FBI Director after Pahalgam attack
 World
World





