HIV, TB and malaria deaths warned to surge heading to human amid Covid-19 pandemic
| Tycoons call for higher taxes to help pay for Covid-19 aid | |
| Israeli scientists use waste to make hand sanitizer for fighting against coronavirus | |
| WAIC 2020: Global AI collaboration to fight pandemic |
Increasing significantly HIV, tuberculosis and malaria deaths amid coronavirus outbreak
According to Times of India, deaths from HIV, tuberculosis and malaria could surge in poor and middle-income countries as already weak health systems grapple with severe disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a predictive study published on Monday.
Over the next five years, deaths from the three diseases could rise by as much as 10%, 20% and 36% respectively - putting the mortality impact on a scale similar to the direct impact of the coronavirus pandemic itself, the modelling study found.
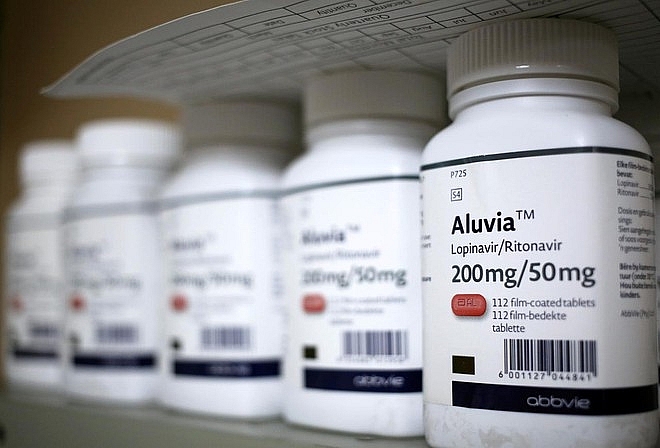 |
| Anti-HIV drugs may be deficient in the Covid-19 pandemic. Photo: Reuters. |
"In countries with a high malaria burden and large HIV and TB epidemics, even short-term disruptions could have devastating consequences for the millions of people who depend on programmes to control and treat these diseases," said Timothy Hallett, a professor at Imperial College London who co-led the work, imperial.ac.uk reported.
He said the knock-on impact of COVID-19 could undo some of the significant progress against these diseases made over the past two decades, "compounding the burden caused by the pandemic directly". But the risks could be mitigated, Hallett said, if countries strive to maintain core health services and deploy preventative measures against infections.
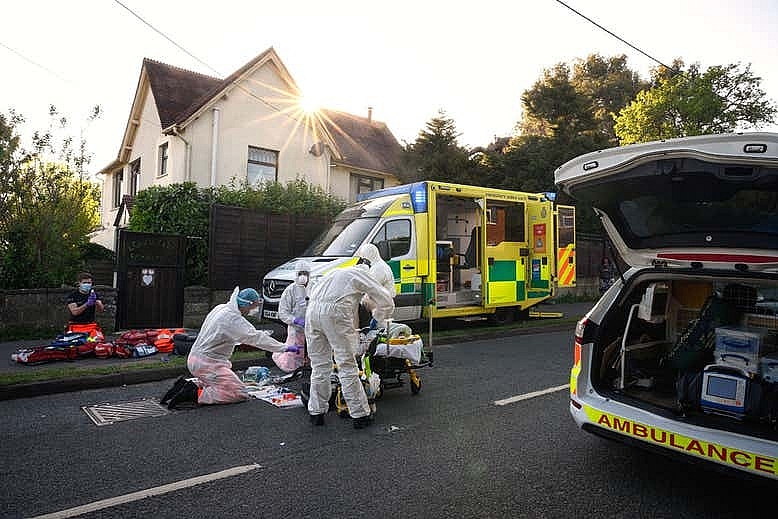 |
| Ambulance crews treat a patient with possible COVID-19 symptoms. As the list of recognised Covid-19 symptoms grows, paramedics are forced to treat every patient as being a potential case. Photo by Leon Neal/POOL/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock . |
Published in the Lancet Global Health journal, the study - which used disease-modelling projections to map out possible COVID-19 pandemic scenarios - found that the greatest impact on HIV would be from interruption to supplies of the antiretroviral AIDS drugs taken by many patients to keep the disease in check, Hindustan Times reported.
The United Nations AIDS agency and the World Health Organization warned last week of such stock shortages, with more than a third of the world's countries already saying they are at risk of running out of antiretrovirals.
With malaria, the study found the largest impact would be due to disrupted distribution of insecticide-treated bed nets, which protect millions of people from becoming infected by malaria-carrying mosquitoes.
How coronavirus make HIV and tuberculosis more deadly
According to New Scientist, for countries with high HIV, TB and malaria rates and weak healthcare systems, “this is right up there in terms of a major priority for how we’re going to combat and minimise the entire risk that the Covid-19 pandemic brings”, says Timothy Hallett at Imperial College London, who led the study. “It’s not piddly in comparison to covid-19, it’s absolutely a priority.”
The new warning is one part of emerging evidence revealing the death and hardship that covid-19 could wreak because of its impact on healthcare services vital for preventing and treating other major epidemics. Malaria, TB and HIV kill around 2.6 million people a year combined.
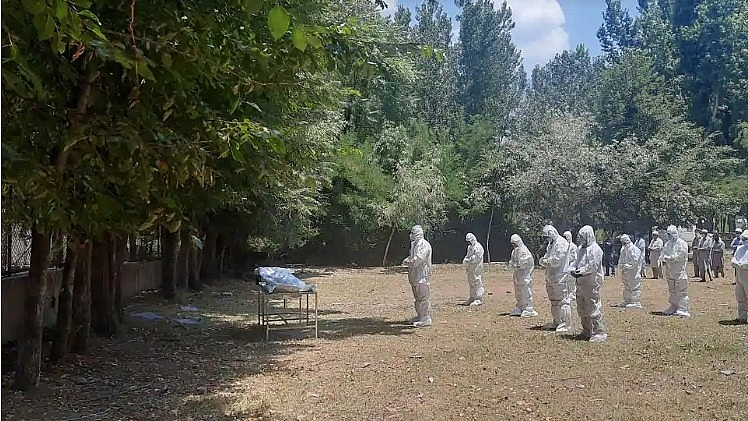 |
| As already weak health systems grapple with severe disruptions from the Covid-19 pandemic, deaths due to other diseases could increase. (Waseem Andrabi/ Hindustan Times) |
The analysis came up with four hypothetical scenarios, based on different interventions in low and middle-income countries. Hallett points out that these scenarios may not come to pass and it is hard to predict how the covid-19 pandemic will unfold.
However, recent history holds precedent for possible knock-on effects. The research was inspired by what was seen during the Ebola outbreak in West Africa between 2014 and 2016, where around half of the deaths were from other diseases as healthcare systems buckled.
The ways in which covid-19 is disrupting health services differ between TB, malaria and HIV, and much of the evidence is anecdotal. Hallett tells of one NGO chartering its own plane from India to bring in generic drugs to Nigeria for HIV treatment, and of drugs stuck in ports globally because customs officials were in lockdown. As early as March, researchers told New Scientist of disruptions to supply chains for malaria nets across Africa.
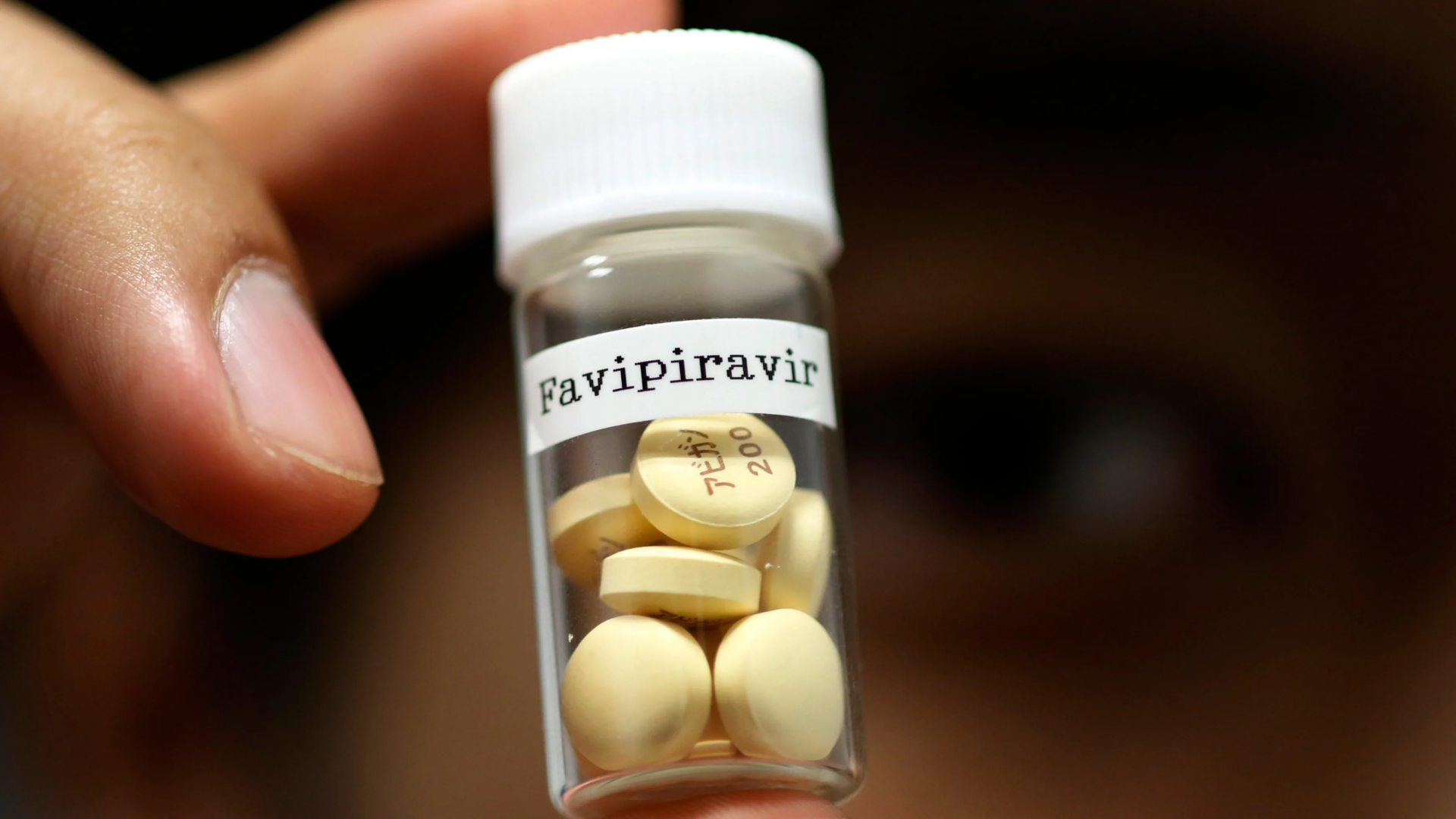 |
| Avigan, the trade name of the drug favipiravir, developed by a subsidiary of Japan's Fujifilm Holdings, has been found effective against COVID-19 in Chinese clinical testing. |
Initial surveys suggest that some health services are struggling. The Global Fund, a crucial financier of programmes to tackle these three illnesses, found in June that 85 per cent of the HIV programmes it funds had seen disruption to delivering their services. For TB programmes, it was 78 per cent, and 73 per cent for malaria programmes.
“I think, at a global level, it’s unprecedented,” says Katherine Atkins at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine regarding the setback for HIV treatment, access to which has been increasing globally in recent years. Despite progress, many countries were already struggling to meet the international 2020 targets for HIV. “This is going to make it worse,” she says.
 |
| Photo: dw.com |
Meg Doherty at the World Health Organization (WHO) says that the impact on HIV services has been “profound”, largely due to disruption of antiretroviral drugs vital for people with the virus. Some suppliers aren’t delivering on time, while lockdowns and travel restrictions have hampered the drugs’ movement between and within countries. Twenty-four nations around the globe have less than three months of the medicines left, says Doherty.
Testing for HIV has also been hampered, meaning an increased risk of transmission because people will be unaware they have it, says Atkins. For TB, which already kills around 4000 people daily, a reduction in diagnosis and treatment is the biggest concern. One study published last month found that without mitigation, there could be more than 200,000 deaths from TB between 2020 and 2024 across China, India and South Africa alone.
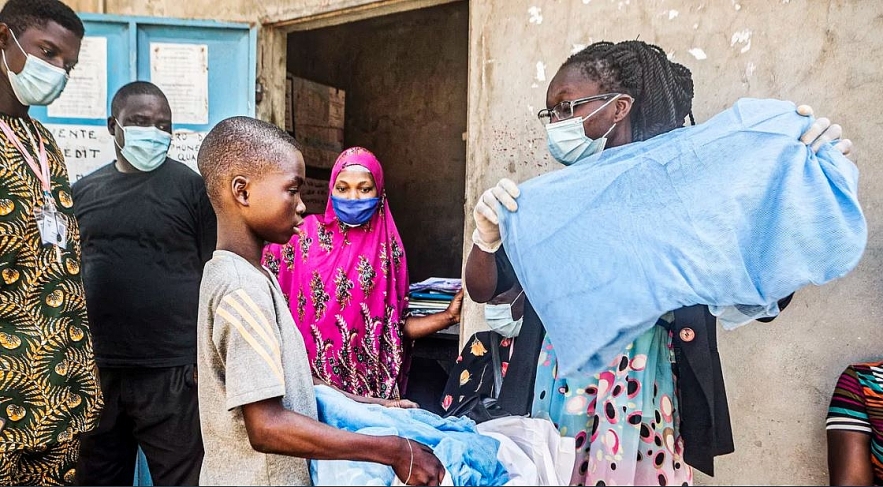 |
| A young boy receives a mosquito net on April 28, 2020 in Benin during a distribution aiming at fighting malaria amid the pandemic of the novel coronavirus. Benin is trying to curb malaria by providing mosquito nets to vulnerable populations as the rainy season approaches. Yanick Folly/AFP via Getty Images |
A common thread across all three epidemics is that people aren’t going to healthcare facilities because they fear catching covid-19 or overwhelming the health system.
“There is a sense of anxiety, there is a sense of concern,” says Salim Abdool Karim at the Centre for the AIDS Programme of Research in South Africa, citing a survey that found 58 per cent of people in South Africa were hesitant to attend healthcare facilities because of the coronavirus. “That’s a major challenge as we grapple with these combined epidemics,” he says.
Key ways to mitigate Covid-19 impacts on services of HIV and tuberculosis
Campaigns encouraging people to overcome those fears will be one of the key ways to mitigate the pandemic’s impact on services for TB, malaria and HIV. Another step is the WHO’s call for healthcare providers to issue multi-month prescriptions of antiretroviral drugs. Yet another measure is simply ensuring that diagnostic facilities remain available, New Scientist reported.
“These things are the things to do. They should have an impact on mitigating. But I don’t know the extent to which they’re all feasible,” says Hallett.
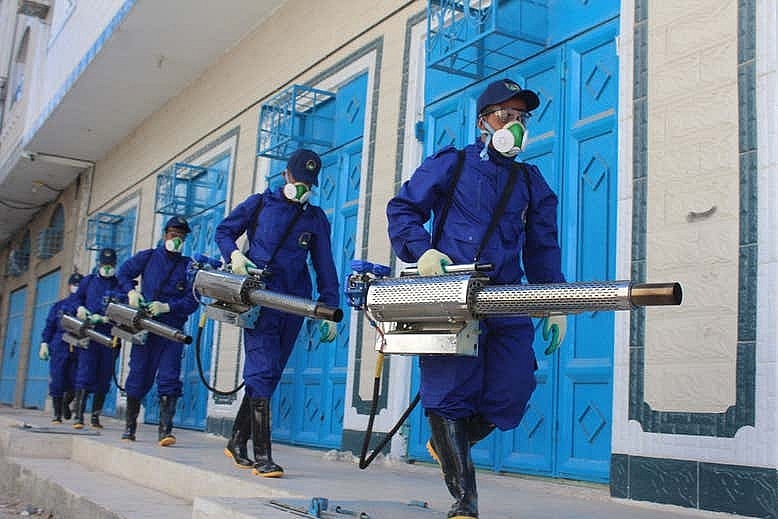 |
| Sanitary workers prepare to perform a fumigation in an area in Aden, Yemen, to help prevent insect-borne diseases such as malaria amid the Covid-19 pandemic. Photo: SALEH AL-OBEIDI/AFP via Getty Images. |
 | World Bank's expert: Strategies to mitigate the public health crisis and prepare for economic revival According to analysis of the World Bank Managing Director of Development Policy and Partnerships, Mari Elka Pangestu, countries and development partners can learn strategies from each other to mitigate ... |
 | Most populous state in Australia closes border for the first time in 100 years Australia closes the border between Australia's two most populous states from July 7 without a proposed schedule time for reopening as this country is scrambling ... |
 | COVID-19 Updates (July 6): Number of Indian detected cases surpasses Russia According to the Worldometers, 11,543,419 COVID-19 cases are reported, including 536,344 deaths and 6,526,679 people recovered. |
Recommended
 World
World
Pakistan NCRC report explores emerging child rights issues
 World
World
"India has right to defend herself against terror," says German Foreign Minister, endorses Op Sindoor
 World
World
‘We stand with India’: Japan, UAE back New Delhi over its global outreach against terror
 World
World
'Action Was Entirely Justifiable': Former US NSA John Bolton Backs India's Right After Pahalgam Attack
Popular article
 World
World
US, China Conclude Trade Talks with Positive Outcome
 World
World
Nifty, Sensex jumped more than 2% in opening as India-Pakistan tensions ease
 World
World
Easing of US-China Tariffs: Markets React Positively, Experts Remain Cautious
 World
World