Utah's Great Salt Lake is Drying Up, Scientists Demand Immediate Actions
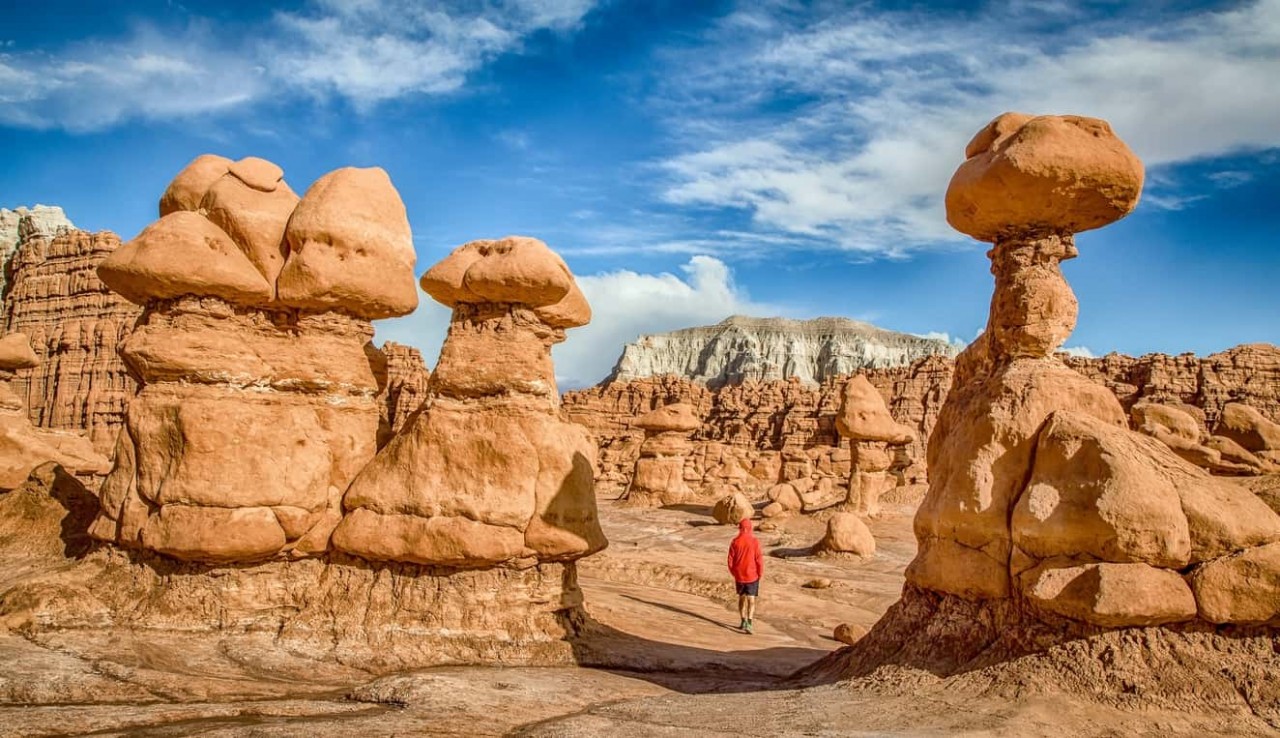
The silvery blue waters of the Great Salt Lake sprawl across the Utah desert, having covered an area nearly the size of Delaware for much of history. For years, though, the largest natural lake west of the Mississippi River has been shrinking. And a drought gripping the American west could make this year the worst yet, according to the Guardian.
The receding water is already affecting the nesting spot of pelicans that are among the millions of birds dependent on the lake. Sailboats have been hoisted out of the water to keep them from getting stuck in the mud. More dry lakebed getting exposed could send arsenic-laced dust into the air that millions breathe.
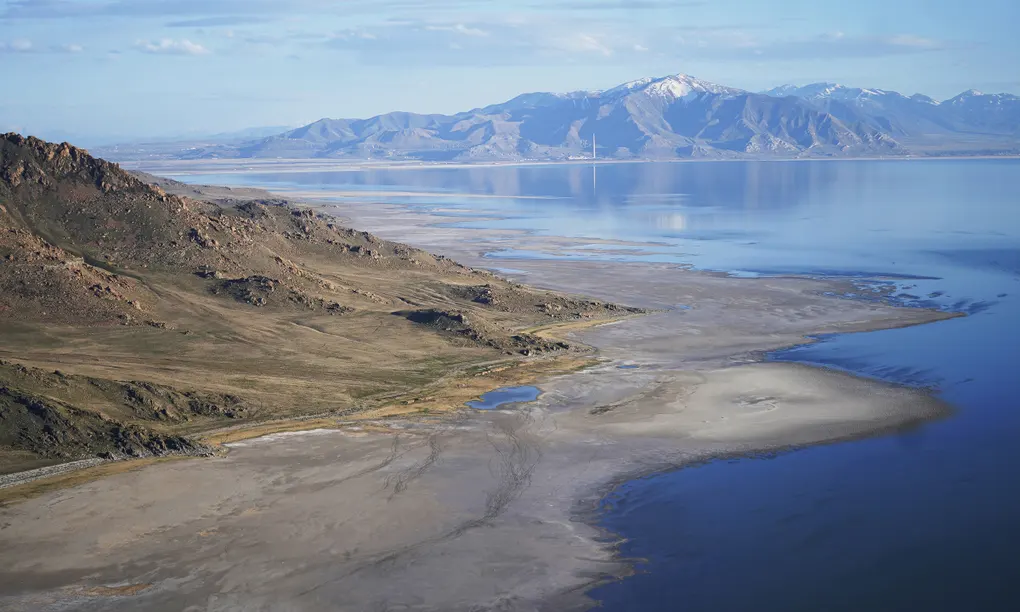 |
| The Great Salt Lake recedes from Anthelope Island in May. Photograph: Rick Bowmer/AP |
“A lot us have been talking about the lake as flatlining,” said Lynn de Freitas, the executive director of Friends of the Great Salt Lake.
The lake’s levels are expected to hit a 170-year low this year. It comes as the drought has the US west bracing for a brutal wildfire season and coping with already low reservoirs. The Utah governor, Republican Spencer Cox, has begged people to cut back on lawn watering and “pray for rain”.
For the Great Salt Lake, though, it is only the latest challenge. People for years have been diverting water from rivers that flow into the lake to water crops and supply homes. Because the lake is shallow, about 35ft (11 meters) at its deepest point, less water quickly translates to receding shorelines.
The largest salt lake in the Western Hemisphere is shrinking rapidly. Left alone, the lake's footprint would span 2,100 square miles -- more than three times the area of Houston. An analysis published last year showed that water siphoned off the rivers that feed the natural wonder had reduced its level by 11 feet, depleting the lake area by more than half.
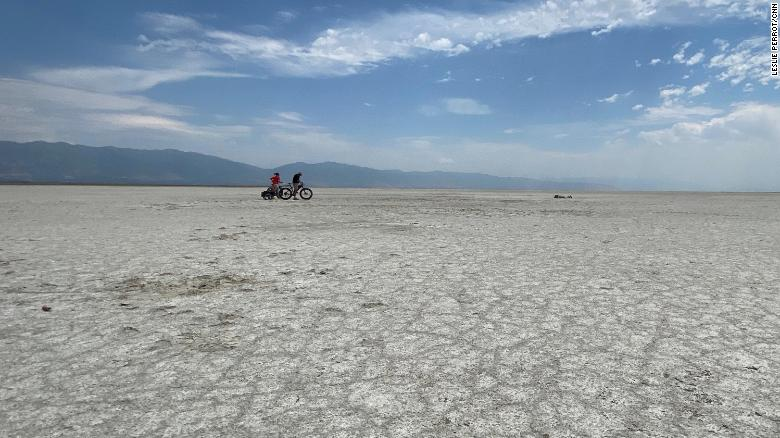 |
| Photo: CNN |
"Twenty years ago, this was under about 10 feet of water," said Kevin Perry, chairman of the department of atmospheric sciences at the University of Utah, as he rode a bike in July across the desiccated lake bed.
Perry warns of what happened at California’s Owens Lake, which was pumped dry to feed thirsty Los Angeles and created a dust bowl that cost millions of dollars to tamp down. The Great Salt Lake is much larger and closer to a populated area, Perry said.
Luckily, much of the bed of Utah’s giant lake has a crust that makes it tougher for dust to blow. Perry is researching how long the protective crust will last and how dangerous the soil’s arsenic may be to people.
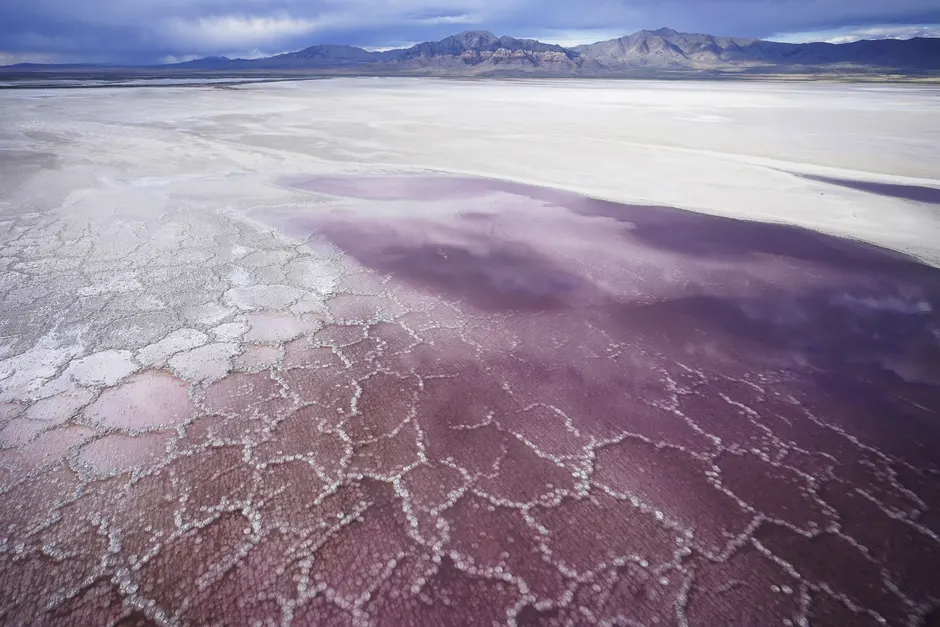 |
| Pink water washes over a salt crust along the receding edge of the Great Salt Lake. Photograph: Rick Bowmer/AP |
This year is primed to be especially bleak. Utah is one of the driest states in the country, and most of its water comes from snowfall. The snowpack was below normal last winter and the soil was dry, meaning much of the melted snow that flowed down the mountains soaked into the ground.
Most years, the Great Salt Lake gains up to 2ft (half a meter) from spring runoff. This year, it was just 6in (15cm), Perry said. “We’ve never had an April lake level that was as low as it was this year,” he said.
Most years, the Great Salt Lake gains up to 2ft (half a meter) from spring runoff. This year, it was just 6in (15cm), Perry said. “We’ve never had an April lake level that was as low as it was this year,” he said.
More exposed lakebed also means more people have ventured on to the crust, including off-road vehicles that damage it, Laura Vernon, the Great Salt Lake coordinator, said.
'We're on the doorstep of a catastrophe'
Huge swaths of the Utah lake look more like Death Valley than any waterway, the ground barren and fractured from dry heat. Other areas look like sprawling street puddles. Birds wade through shoreline muck along empty marinas, their slips sagging to the ground.
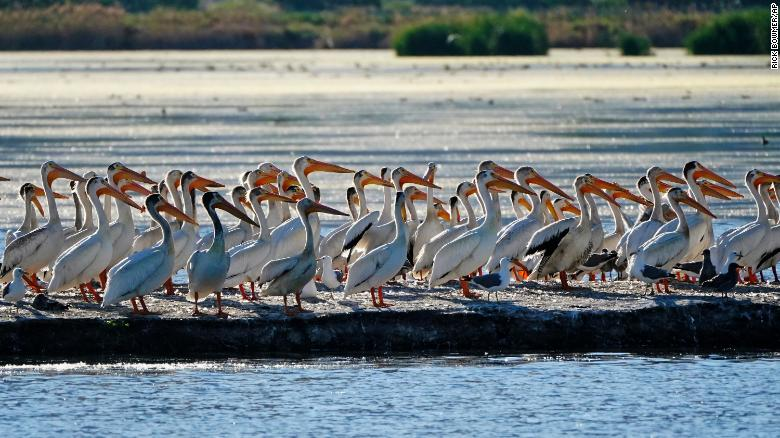 |
| Pelicans gather in June on an island on Farmington Bay near the Great Salt Lake. Photo: CNN |
"The saltiest sailors on the planet have had their sailboats hoisted out of the Great Salt Lake's marinas by crane in recent days, due to dropping Lake levels," the Utah Rivers Council wrote in the introduction of a report warning that a dam, pipeline and reservoir proposal to the east will only compound problems, CNN reported.
While human behavior remains scientists' primary concern, the lack of rain out West isn't helping. Great Salt Lake now is like water sitting in a plate, whereas most lakes resemble a cup, said Jaimi Butler, co-editor of the 2020 analysis showing the lake area had shrunk by 51%.
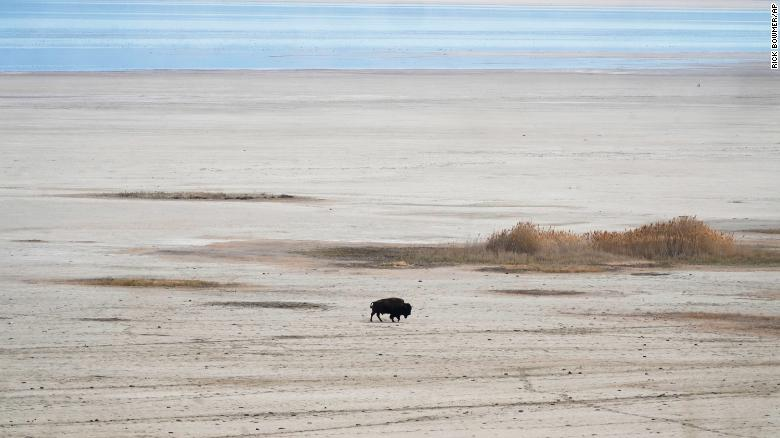 |
| A bison walks in April along the receding edge of the Great Salt Lake on its way to a watering hole at Antelope Island, Utah. Photo: CNN |
The shallow waters are more prone to evaporation in drought conditions, and while the lake's level ebbs and flows over any given year, the lake tends to reach its low point in the fall, around October. The lake will continue to drop and shrink over the next three months, and the water level could sink as much as 2 more feet by Halloween, Butler suspects.
"Keeping water in Great Salt Lake is the biggest thing that keeps me up at night," said Butler, a wildlife biologist who grew up around the lake and serves as coordinator for the Great Salt Lake Institute at Westminster College. "We're on the doorstep of a catastrophe."
 | China signs pact to share year-round water data with Mekong River Commission China has agreed to provide the Mekong River Commission (MRC) with year-round hydrological data, contributing to better river monitoring and flood and drought forecasting in ... |
 | PM calls for advanced solutions and long-term vision for Mekong Delta to deal with climate change Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc called for a long-term vision to cope with drought and salt intrusion during the Mekong Delta’s dry season, which normally ... |
 | India funds seven water management projects in four Vietnam's Mekong Delta provinces Seven memoranda of understanding (MoUs) were signed between Government of India and four southern Provinces of Vietnam — Ben Tre, Hau Giang, Kien Giang and ... |
Recommended
 World
World
India reports 9 Pakistani Aircraft Destroyed In Operation Sindoor Strikes
 World
World
Thailand Positions Itself As a Global Wellness Destination
 World
World
Indonesia Accelerates Procedures to Join OECD
 World
World
South Korea elects Lee Jae-myung president
Popular article
 World
World
22nd Shangri-La Dialogue: Japan, Philippines boost defence cooperation
 World
World
Pakistan NCRC report explores emerging child rights issues
 World
World
"India has right to defend herself against terror," says German Foreign Minister, endorses Op Sindoor
 World
World










