TRUST: The most powerful weapon of Vietnam to control COVID-19 pandemic
The public trust in the Vietnamese media
When coping with a new problem, we look for information to evaluate our options and the COVID-19 pandemic was no exception.
During times of chaos and unpredictability, our emotions may cloud our fact-checking abilities, and finding an authority to provide fast and trustworthy information becomes more vital than ever.
When it comes to information credibility, the media has proved to be this authority in Vietnam; it has been essential to preventing the spread ofCOVID-19by providing trustworthy and detailed information daily on new COVID-19 cases from the National Steering Committee for COVID-19 Prevention and Control.
One of the biggest mainstream media channels, Tuoi Tre launched the news section Fake-True to fact check accurate and untrue information being circulated on social media platforms.
The Vietnamese mainstream media also fact checked its information, flagging what was not true, and sharing a variety of content that wasn’t only limited to the potential health impacts of the virus.
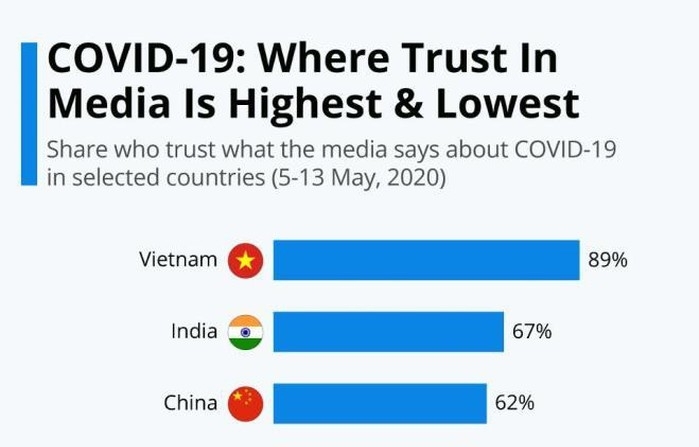
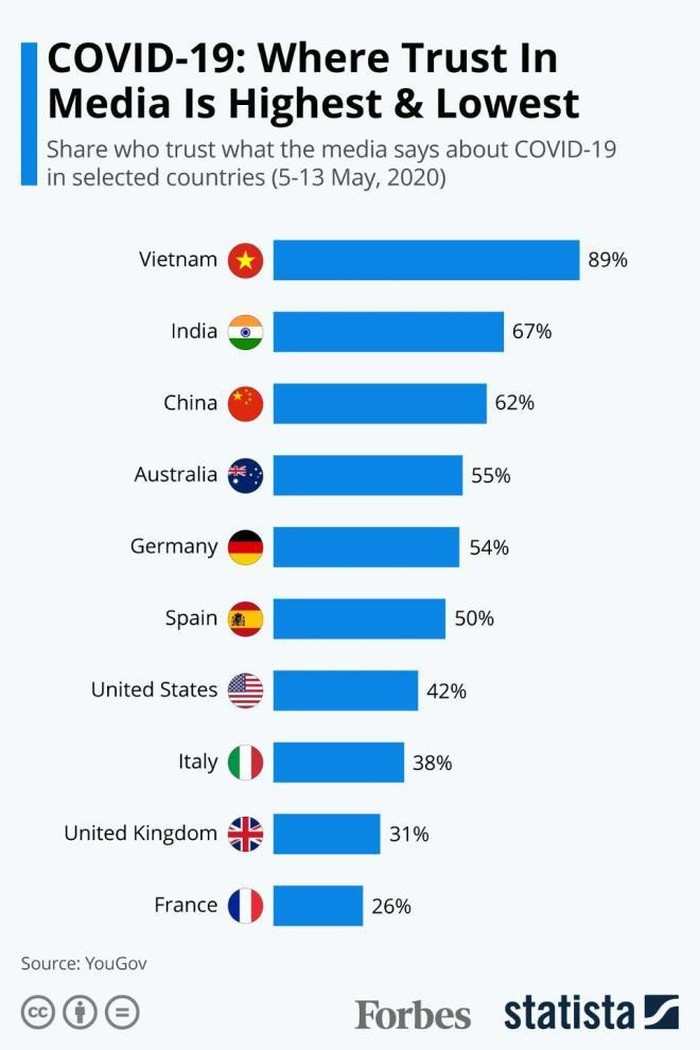
Through its actions, the media in Vietnam enhanced its reputation as a reliable source of information during uncertain times. This trust was reflected by a recent YouGov survey (5-13 May 2020) that showed Vietnam had the highest level of public trust (89 per cent) in the media among the 26 countries studied in the research.
 |
| The media in Vietnam enhanced its reputation as a reliable source of information during the outbreak. Photo: news.un.org |
The public trust in the community and government
As of 18 June 2020, there were 335 COVID-19 cases and zero deaths in a country that represents 1.25 per cent of the total world population. This success was due to many factors - including the actions the government took - however in order for these actions to be successful, the government needed to trust its people to do the right thing. This would not have been possible without the trust of the people in the community, the media, and the Vietnam government.
In a TV interview with 7News Australia, the Australian Chamber of Commerce secretary in Vietnam Matt Young said “the Vietnamese community came together as a community and looked after each other”.
In addition to providing daily detailed, timely and accurate information to the nation, the government also worked to stop the spread of misinformation. In a new decree announced in February 2020, a fine of 10-20 million VND was imposed on anyone using social media to share false, untruthful, distorted or slanderous information.
Authorities also launched a public campaign to build awareness and understanding of the consequences of misinformation with the slogan “Fake news, real consequences”.
 |
| Posters with the slogan “Fake news, real consequences” at a local health center. Photo: Tony Nguyen |
The public trust in social media vs traditional media
According to the Pew Research Centre’s study of 2017, a majority of people get their news from daily online sources, and Vietnam is no exception. Whether information is believed to be true or inaccurate can be influenced by many factors including the trust someone has for the source of the information.
Social media has given a platform to many individuals who have neither the knowledge nor the subject matter experience to provide credible and specific information.
According to a report from the Center for Countering Digital Hate, more than 90 per cent of posts spreading disinformation about COVID-19remained visible after being reported on Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
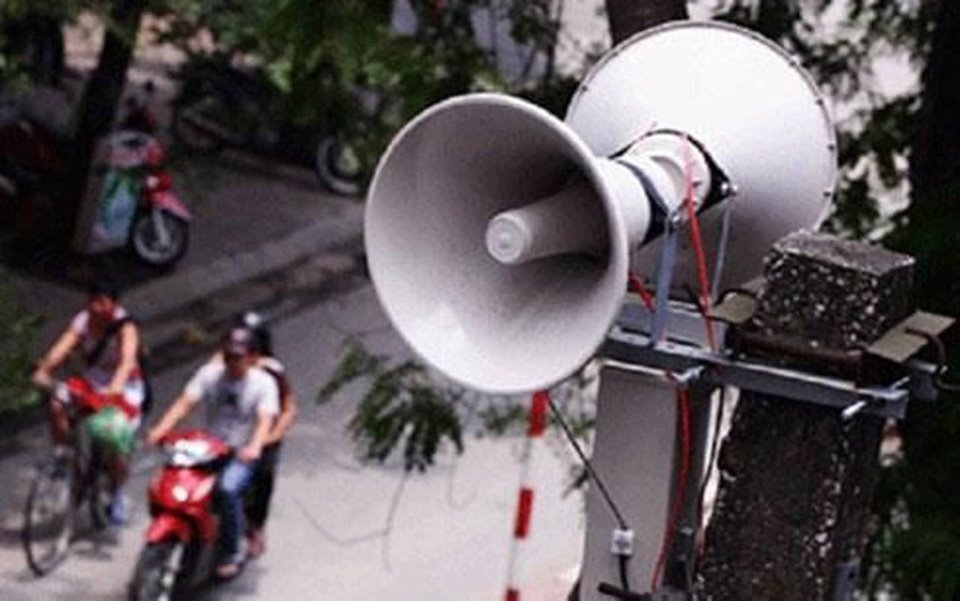 |
| Vietnam’s public loudspeaker system: a means of communication to combat COVID-19. Photo: baobaclieu |
Social media platforms received 649 reported posts from 20 April to 26 May 2020, but the action was taken on only 61 (9.4 per cent) of the posts. Of those, 6.3 per cent of posts were removed, 2 per cent were from accounts that were subsequently taken down, and 1 per cent was flagged as false information but remained published.
Social media channels with citizen journalism have not replaced professional and governmental media channels when it comes to trusted information in the minds of the public. The latter has become undeniably essential, and ignoring their impact is a mistake that can cost governments not only its people’s trust but also their lives.
 |
| Social media has given a platform to many individuals to access to information during the pandemic. Photo: msutoday |
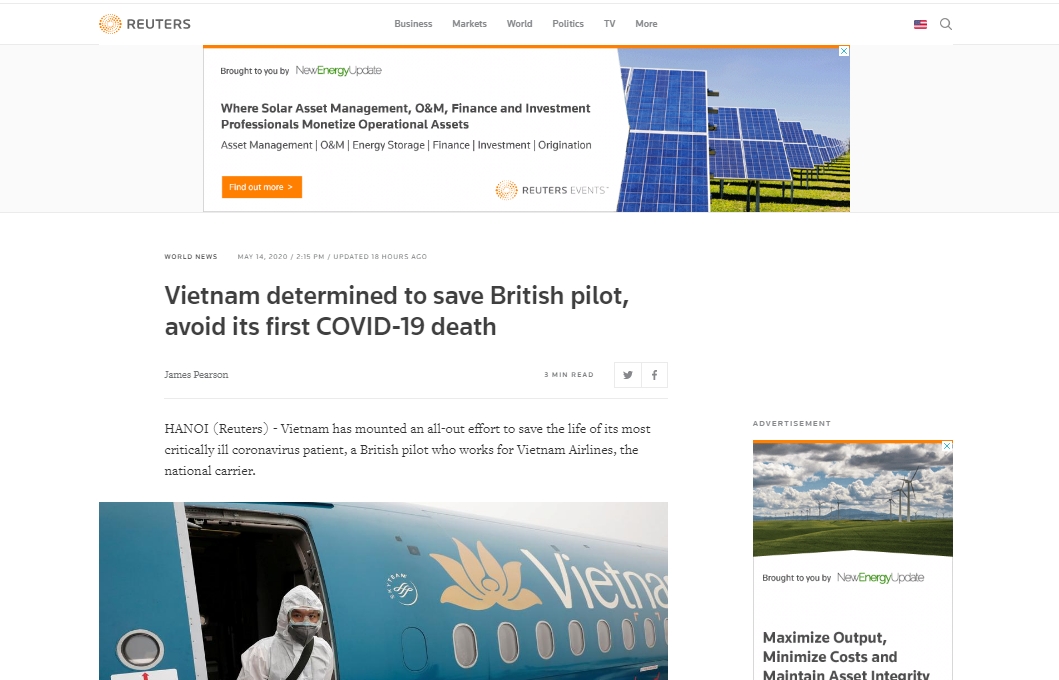 | Reuters lauds Vietnam’s determination to save the critical COVID-19 British pilot Reuters on Thursday runs an article claiming “Vietnam has mounted an all-out effort to save the life of the British pilot, its most critically ill ... |
 | Covid-19 combat in Vietnam: Immediacy, effectiveness, and transparency! Shama Obaed, a member of the Foreign Relations Committee, Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) has shared his point of view on the coronavirus fight in Vietnam ... |
 | International media lauds Vietnam’s ‘Rice ATM’ The “Rice ATM” dispensing bagful of rice for vulnerable populations during coronavirus lockdown that first appeared in HCMC early April has greatly drawn international attention. ... |
Recommended
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
Hanoi, South Africa Strengthens People-to-people Exchanges, Expands Multi-sector Cooperation
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
Hue City to Raise Awareness on Mine Accident Prevention
 Focus
Focus
Vietnam Leaves Imprints on the World Peacekeeping Map
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
“Global Vietnamese Singing 2025” - Connecting Hearts Longing for Homeland
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
Vietnam’s People's Public Security Force Actively Contributes to UN Peacekeeping Operations
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
HAUFO Enhances Competence of People-to-People Diplomacy Personnel
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home
Hands that Reserve Da Long Brocade Craft
 Viet's Home
Viet's Home